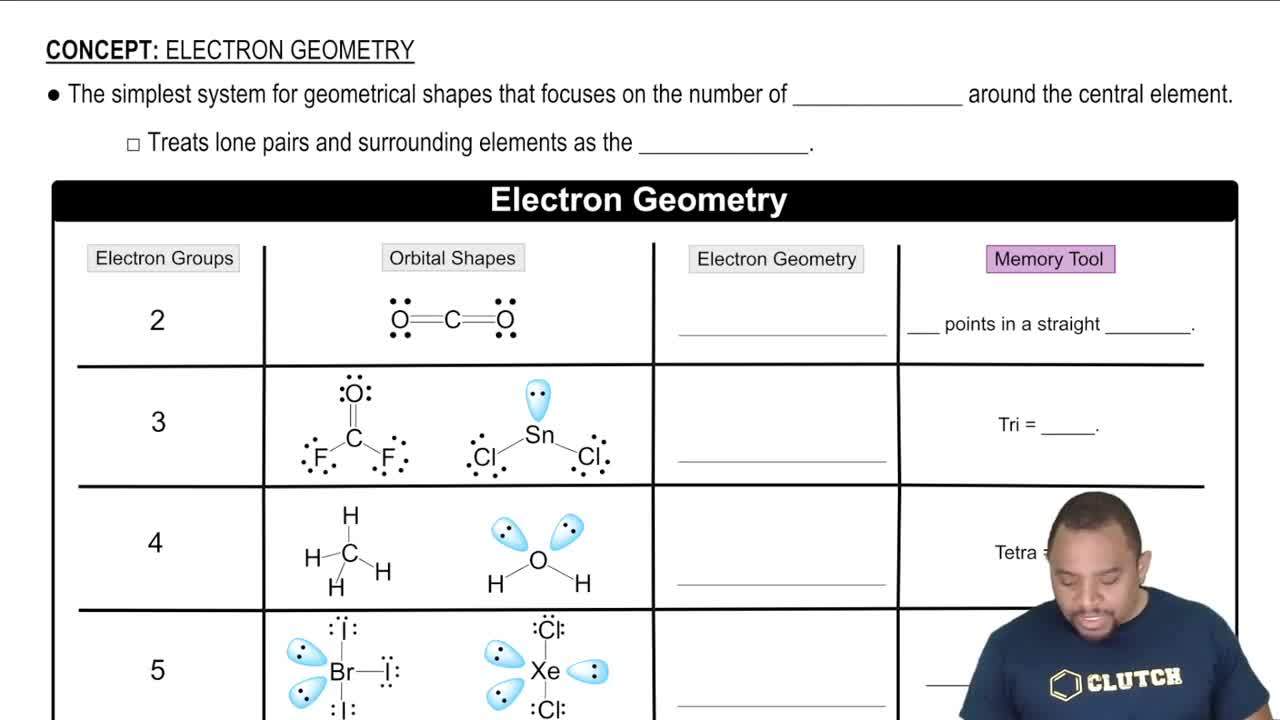
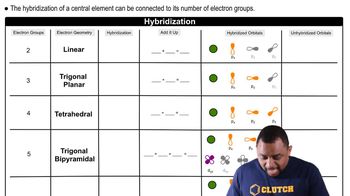
The following three Lewis structures can be drawn for N2O:
(b) The N—N bond length in N2O is 1.12 Å, slightly longer than a typical N≡N bond; and the N—O bond length is 1.19 Å, slightly shorter than a typical N═O bond (see Table 8.4). Based on these data, which resonance structure best represents N2O?