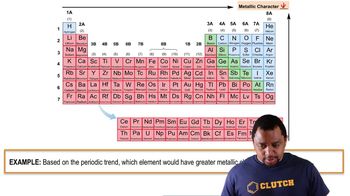
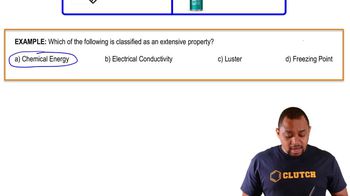
Textbook Question
Consider the following equation:Al3+1g2 + e-¡Al2+1g2Which of the following statements are true? (i) The energychange for this process is the second electron affinity of Alatom since Al2+1g2 is formed. (ii) The energy change for thisprocess is the negative of the third ionization energy of the Alatom. (iii) The energy change for this process is the electronaffinity of the Al2+ ion.