Hydrogen is an unusual element because it behaves in some ways like the alkali metal elements and in other ways like nonmetals. Its properties can be explained in part by its electron configuration and by the values for its ionization energy and electron affinity. (a) Explain why the electron affinity of hydrogen is much closer to the values for the alkali elements than for the halogens.
Ch.7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 7, Problem 101
It is possible to define metallic character as we do in this book and base it on the reactivity of the element and the ease with which it loses electrons. Alternatively, one could measure how well electricity is conducted by each of the elements to determine how 'metallic' the elements are. On the basis of conductivity, there is not much of a trend in the periodic table: Silver is the most conductive metal, and manganese the least. Look up the first ionization energies of silver and manganese; which of these two elements would you call more metallic based on the way we define it in this book?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
First, recall that the first ionization energy is the energy required to remove the most loosely held electron from an atom. In other words, it's the energy needed to make an atom lose one electron and become a positive ion.
Next, remember that metallic character is defined by how easily an element can lose its electrons. The easier it is for an element to lose its electrons, the more metallic it is.
Then, look up the first ionization energies of silver and manganese. You can find these values in a reference book or online. The element with the lower first ionization energy is the one that loses its electrons more easily.
Compare the first ionization energies of silver and manganese. The element with the lower first ionization energy is more metallic according to the definition given in the book.
Finally, based on the comparison, determine which of the two elements, silver or manganese, is more metallic.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Metallic Character
Metallic character refers to the set of properties associated with metals, including their ability to lose electrons easily, conduct electricity, and exhibit malleability and ductility. In the context of the periodic table, metallic character generally increases down a group and decreases across a period. This concept is crucial for understanding the reactivity of elements and their placement in the periodic table.
Recommended video:
Guided course
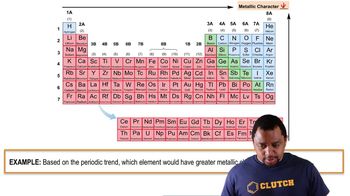
Metallic Character Example
Ionization Energy
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in its gaseous state. It is a key factor in determining an element's metallic character; elements with lower ionization energies tend to lose electrons more easily, making them more metallic. Comparing the first ionization energies of silver and manganese helps to assess their metallic character based on the defined criteria.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ionization Energy
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct electric current, which is a significant property of metals. While conductivity can indicate metallic character, it does not always correlate directly with reactivity or ionization energy. Understanding the differences between conductivity and other properties like ionization energy is essential for accurately determining the metallic nature of elements.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Extensive Property Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The first ionization energy of the oxygen molecule is the energy required for the following process: O21g2¡O2 +1g2 + e- The energy needed for this process is 1175 kJ>mol, very similar to the first ionization energy of Xe. Would you expect O2 to react with F2? If so, suggest a product or products of this reaction.
1
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following is the expected product of the reaction of K(s) and H2(g)? (i) KH(s), (ii) K2H(s), (iii) KH2(s), (iv) K2H2(s), or (v) K(s) and H2(g) will not react with one another.
1
views
