
Suppose that the spin quantum number, ms, could have three allowed values instead of two. How would this affect the number of elements in the first four rows of the periodic table?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Quantum Numbers
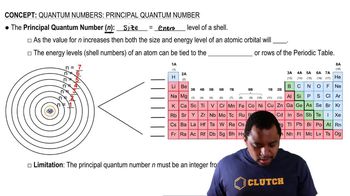
Electron Configuration
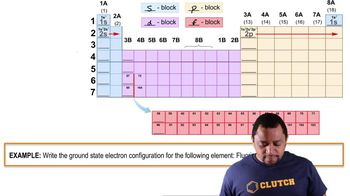
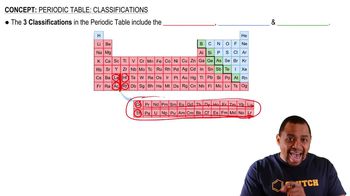
Periodic Table Structure
The Chemistry and Life box in Section 6.7 described the techniques called NMR and MRI. (a) Instruments for obtaining MRI data are typically labeled with a frequency, such as 600 MHz. In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum does a photon with this frequency belong?
The Chemistry and Life box in Section 6.7 described the techniques called NMR and MRI. (c) When the 450-MHz photon is absorbed, does it change the spin of the electron or the proton on a hydrogen atom?
Using the periodic table as a guide, write the condensed electron configuration and determine the number of unpaired electrons for the ground state of (a) Cl (b) Al (c) Zr (d) As (e) Sb (f) W.
Scientists have speculated that element 126 might have a moderate stability, allowing it to be synthesized and characterized. Predict what the condensed electron configuration of this element might be.
In the experiment shown schematically below, a beam of neutral atoms is passed through a magnetic field. Atoms that have unpaired electrons are deflected in different directions in the magnetic field depending on the value of the electron spin quantum number. In the experiment illustrated, we envision that a beam of hydrogen atoms splits into two beams. (a) What is the significance of the observation that the single beam splits into two beams?
