(c) The laser pointer emits light because electrons in the material are excited (by a battery) from their ground state to an upper excited state. When the electrons return to the ground state, they lose the excess energy in the form of 532-nm photons. What is the energy gap between the ground state and excited state in the laser material?

One type of sunburn occurs on exposure to UV light of wavelength in the vicinity of 325 nm. (a) What is the energy of a photon of this wavelength?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Photon Energy
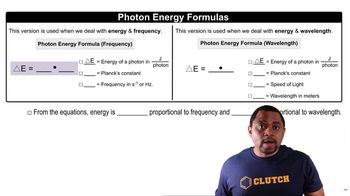
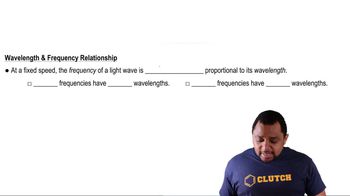
Wavelength and Frequency Relationship
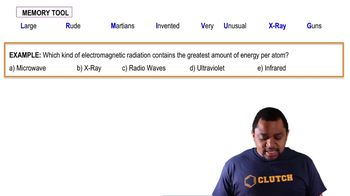
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation
An AM radio station broadcasts at 1000 kHz and its FM partner broadcasts at 100 MHz. Calculate and compare the energy of the photons emitted by these two radio stations.
One type of sunburn occurs on exposure to UV light of wavelength in the vicinity of 325 nm. (b) What is the energy of a mole of these photons?
One type of sunburn occurs on exposure to UV light of wavelength in the vicinity of 325 nm. (c) How many photons are in a 1.00 mJ burst of this radiation?
One type of sunburn occurs on exposure to UV light of wavelength in the vicinity of 325 nm. (d) These UV photons can break chemical bonds in your skin to cause sunburn—a form of radiation damage. If the 325-nm radiation provides exactly the energy to break an average chemical bond in the skin, estimate the average energy of these bonds in kJ/mol.
