Consider the two waves shown here, which we will consider to represent two electromagnetic radiations: (b) What is the frequency of wave A?

Certain elements emit light of a specific wavelength when they are burned or heated in a non-luminous flame. Historically, chemists used such emission wavelengths to determine whether specific elements were present in a sample. Some characteristic wavelengths for a few of the elements are given in the following table: Ag 328.1 nm Fe 372.0 nm Au 267.6 nm K 404.7 nm Ba 455.4 nm Mg 285.2 nm Ca 422.7 nm Na 589.6 nm Cu 324.8 nm Ni 341.5 nm (a) Determine which of these emissions occur in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
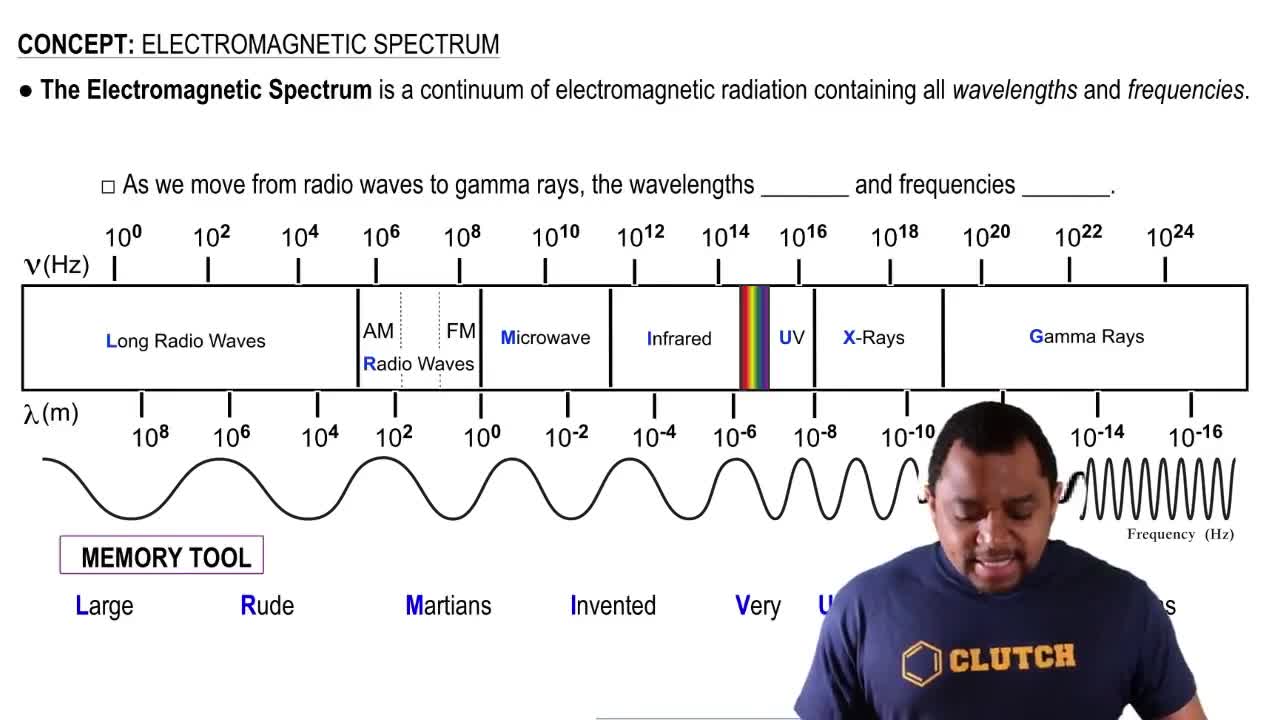
Electromagnetic Spectrum
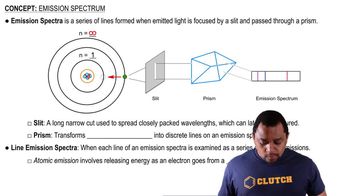
Emission Spectra
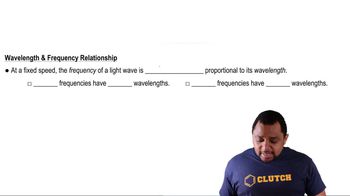
Wavelength and Energy Relationship
If a sample of calcium chloride is introduced into a nonluminous flame, the color of the flame turns to orange ('flame test'). The light is emitted because calcium atoms become excited; their return to the ground state results in light emission. (b) What is the energy of 1.00 mol of these photons (a mole of photons is called an Einstein)?
If a sample of calcium chloride is introduced into a nonluminous flame, the color of the flame turns to orange (“flame test”). The light is emitted because calcium atoms become excited; their return to the ground state results in light emission. (c) Calculate the energy gap between the excited and ground states for the calcium atom.
Certain elements emit light of a specific wavelength when they are burned or heated in a non-luminous flame. Historically, chemists used such emission wavelengths to determine whether specific elements were present in a sample. Some characteristic wavelengths for a few of the elements are given in the following table: Ag 328.1 nm Fe 372.0 nm Au 267.6 nm K 404.7 nm Ba 455.4 nm Mg 285.2 nm Ca 422.7 nm Na 589.6 nm Cu 324.8 nm Ni 341.5 nm (c) When burned, a sample of an unknown substance is found to emit light of frequency 6.58 × 1014 s-1. Which of these elements is probably in the sample?
In January 2006, the New Horizons space probe was launched from Earth with the mission to perform a flyby study of Pluto. The arrival at the dwarf planet was estimated to happen after nine years, in 2015. The distance between Earth and Pluto varies depending on the location of the planets in their orbits, but at their closest, the distance is 4.2 billion kilometers (2.6 billion miles). Calculate the minimum amount of time it takes for a transmitted signal from Pluto to reach the Earth.
