(c) Would the radiations in part (a) or part (b) be detected by an X-ray detector?
Ch.6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 6, Problem 21b
A laser pointer used in a lecture hall emits light at 650 nm. Using Figure 6.4, predict the color associated with this wavelength.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given wavelength of the laser pointer, which is 650 nm.
Understand that visible light is part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which ranges from approximately 400 nm to 700 nm.
Recall that different wavelengths within the visible spectrum correspond to different colors.
Consult Figure 6.4 or a similar reference that maps specific wavelength ranges to colors in the visible spectrum.
Determine the color associated with the 650 nm wavelength by locating it within the red region of the visible spectrum.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
38sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which ranges from approximately 400 nm (violet) to 700 nm (red). Each wavelength corresponds to a specific color perceived by the human eye. Understanding where 650 nm falls within this spectrum is essential for predicting the color emitted by the laser pointer.
Recommended video:
Guided course
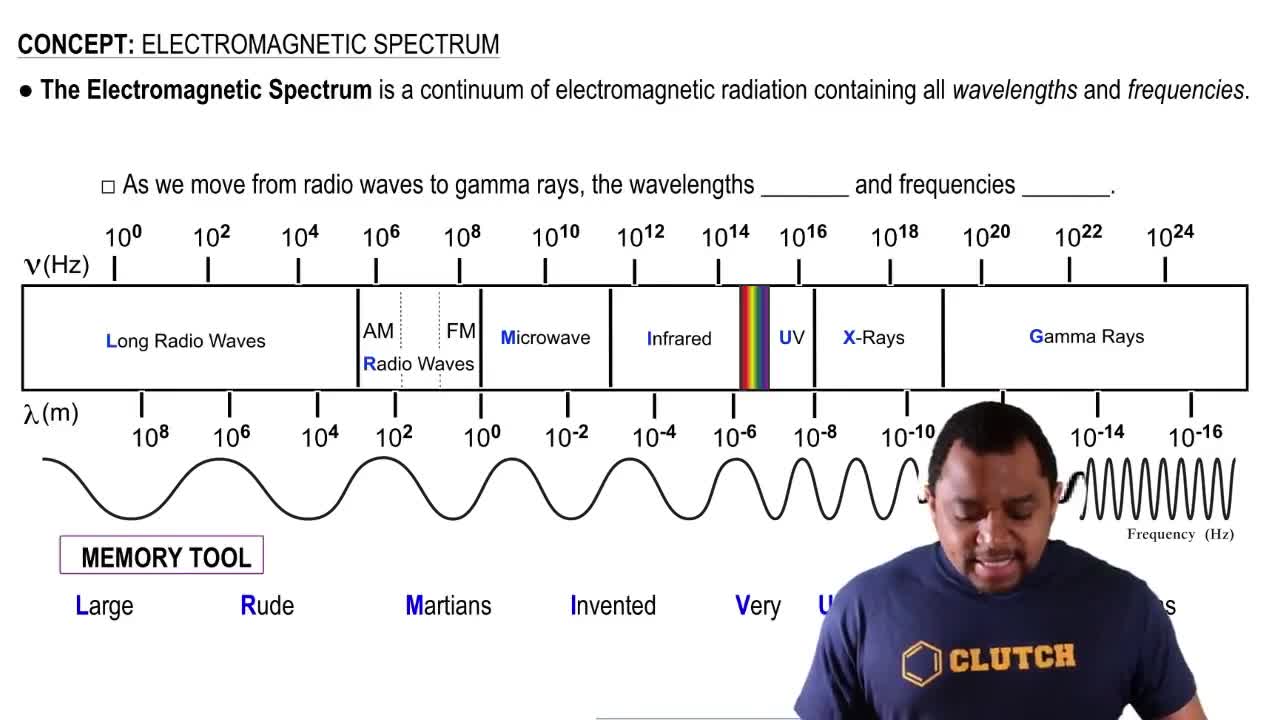
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Wavelength and Color Perception
Wavelength is a key factor in determining the color of light. In the visible spectrum, shorter wavelengths correspond to colors like violet and blue, while longer wavelengths correspond to red. At 650 nm, the light emitted by the laser pointer is in the red region of the spectrum, which is crucial for accurately identifying the color associated with this wavelength.
Recommended video:
Guided course
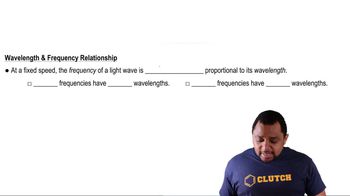
Frequency-Wavelength Relationship
Color Mixing and Perception
Color perception is influenced by how different wavelengths of light mix and how they are interpreted by the human eye. The primary colors of light (red, green, and blue) combine in various ways to produce other colors. In the case of a laser pointer emitting light at 650 nm, the direct perception of red light is straightforward, as it does not involve mixing with other colors.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Scientific Notation Mixed Operations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(d) What distance does electromagnetic radiation travel in 0.38 ps?
Textbook Question
A laser pointer used in a lecture hall emits light at 650 nm. What is the frequency of this radiation?
Textbook Question
It is possible to convert radiant energy into electrical energy using photovoltaic cells. Assuming equal efficiency of conversion, would infrared or ultraviolet radiation yield more electrical energy on a per-photon basis?
2
views
Textbook Question
If human height were quantized in 1-cm increments, what would happen to the height of a child as she grows up: (i) the child's height would never change, (ii) the child's height would continuously increase, (iii) the child's height would increase in jumps of 6 cm, or (iv) the child's height would increase in 'jumps' of 1 cm at a time?
1
views
Textbook Question
Einstein's 1905 paper on the photoelectric effect was thefirst important application of Planck's quantum hypothesis.Describe Planck's original hypothesis, and explain howEinstein made use of it in his theory of the photoelectriceffect.
