Atomic hydrogen (H) is used in welding (AHW). The atoms recombine to hydrogen molecules with a large release of heat according to the following reaction: 2 H(g) → H2(g) (b) Which has the higher enthalpy under these conditions, 2 H(g) or H2(g)?
Ch.5 - Thermochemistry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 5, Problem 42c,d
Without referring to tables, predict which of the following has the higher enthalpy in each case: (c) 1 mol I2(g) and 1 mol H2(g) at 25 °C or 2 mol HI(g) at 25 °C (d) 1 mol H2(g) at 100 °C or 1 mol H2(g) at 300 °C.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the chemical reaction involved: I_2(g) + H_2(g) -> 2 HI(g).
Understand that enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system, often associated with the heat content.
Recognize that the formation of bonds releases energy (exothermic), while breaking bonds requires energy (endothermic).
Consider the bond energies: breaking the I-I and H-H bonds requires energy, while forming two H-I bonds releases energy.
Predict that the enthalpy of the products (2 mol HI) is lower than the enthalpy of the reactants (1 mol I_2 and 1 mol H_2) because the formation of HI releases more energy than is required to break the I_2 and H_2 bonds.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Enthalpy of Formation
Enthalpy of formation refers to the change in enthalpy when one mole of a compound is formed from its elements in their standard states. It is a crucial concept in thermodynamics, as it helps predict the stability and energy content of compounds. For example, the formation of hydrogen iodide (HI) from hydrogen (H2) and iodine (I2) involves specific enthalpy changes that can be compared to the enthalpy of the reactants.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Enthalpy of Formation
Bond Energies
Bond energies represent the amount of energy required to break a bond between two atoms in a molecule. The strength of these bonds directly influences the enthalpy of a substance; stronger bonds typically correlate with lower enthalpy. In the case of HI, the bond energy between H and I will affect the overall enthalpy when comparing it to the elemental gases I2 and H2.
Recommended video:
Guided course
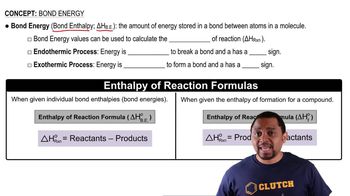
Bond Energy
Hess's Law
Hess's Law states that the total enthalpy change for a chemical reaction is the same, regardless of the number of steps taken to achieve the reaction. This principle allows for the calculation of enthalpy changes by summing the enthalpy changes of individual steps. In this question, Hess's Law can be applied to compare the enthalpy of the reactants (I2 and H2) with the product (HI) to determine which has a higher enthalpy.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Hess's Law
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Without referring to tables, predict which of the following has the higher enthalpy in each case: (a) 1 mol I2(s) or 1 mol I2(g) at the same temperature
Textbook Question
Without referring to tables, predict which of the following has the higher enthalpy in each case: (b) 2 mol of iodine atoms or 1 mol of I2
1
views
Textbook Question
Consider the following reaction: 2 CH3OH(g) → 2 CH4(g) + O2(g) ΔH = +252.8 kJ (b) Calculate the amount of heat transferred when 24.0 g of CH3OH(g) is decomposed by this reaction at constant pressure.
Textbook Question
Consider the following reaction: 2 CH3OH(g) → 2 CH4(g) + O2(g) ΔH = +252.8 kJ (c) For a given sample of CH3OH, the enthalpy change during the reaction is 82.1 kJ. How many grams of methane gas are produced?
