A gas is confined to a cylinder under constant atmospheric pressure, as illustrated in Figure 5.4. When 0.49 kJ of heat is added to the gas, it expands and does 214 J of work on the surroundings. What are the values of H and E for this process?
Ch.5 - Thermochemistry

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 5, Problem 39a
The complete combustion of methane, CH4(g), to form H2O(l) and CO2(g) at constant pressure releases 890 kJ of heat per mole of CH4. (a) Write a balanced thermochemical equation for this reaction.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the reactants and products in the combustion of methane. Methane (CH4) reacts with oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O).
Write the unbalanced chemical equation for the combustion of methane: CH4(g) + O2(g) -> CO2(g) + H2O(l).
Balance the chemical equation. Start by balancing the carbon atoms: CH4(g) + O2(g) -> CO2(g) + H2O(l). Since there is one carbon atom in CH4 and one in CO2, the carbon is already balanced.
Next, balance the hydrogen atoms. There are 4 hydrogen atoms in CH4, so you need 2 H2O molecules to balance the hydrogen: CH4(g) + O2(g) -> CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l).
Finally, balance the oxygen atoms. There are 2 oxygen atoms in CO2 and 2 in 2 H2O, totaling 4 oxygen atoms needed. Therefore, you need 2 O2 molecules: CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) -> CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l). Include the enthalpy change: CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) -> CO2(g) + 2 H2O(l) ΔH = -890 kJ/mol.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Balanced Chemical Equation
A balanced chemical equation represents a chemical reaction with equal numbers of each type of atom on both sides of the equation. This ensures the law of conservation of mass is upheld, meaning that matter is neither created nor destroyed in the reaction. For combustion reactions, it is essential to balance the reactants and products, including the correct stoichiometric coefficients for all species involved.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Thermochemical Equation
A thermochemical equation includes not only the balanced chemical equation but also the heat change associated with the reaction. It indicates whether the reaction is exothermic (releases heat) or endothermic (absorbs heat). In this case, the combustion of methane is exothermic, releasing 890 kJ of heat per mole of CH4, which should be included in the equation.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Thermochemical Equations
Combustion Reaction
A combustion reaction is a type of chemical reaction where a substance (usually a hydrocarbon) reacts with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy in the form of heat and light. In the case of methane, the complete combustion involves the reaction of CH4 with O2 to yield CO2 and H2O, making it a key example of an exothermic reaction in organic chemistry.
Recommended video:
Guided course
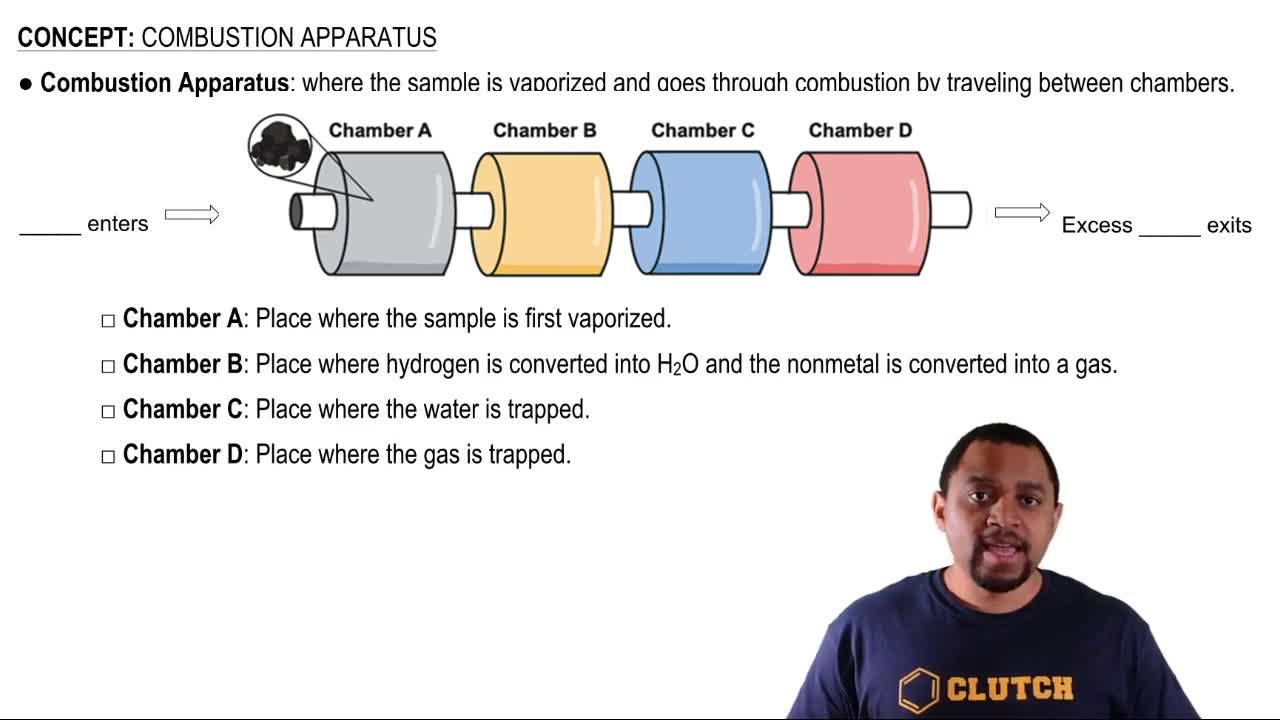
Combustion Apparatus
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
The complete combustion of methane, CH4(g), to form H2O(l) and CO2(g) at constant pressure releases 890 kJ of heat per mole of CH4. (b) Draw an enthalpy diagram for the reaction.
Textbook Question
The decomposition of sodium bicarbonate (baking soda), NaHCO3(s), into Na2CO3(s), H2O(l), and CO2(g) at constant pressure requires the addition of 85 kJ of heat per two moles of NaHCO3. (a) Write a balanced thermochemical equation for the reaction.
Textbook Question
Atomic hydrogen (H) is used in welding (AHW). The atoms recombine to hydrogen molecules with a large release of heat according to the following reaction: 2 H(g) → H2(g) (a) Using the thermodynamic data in Appendix C, calculate the enthalpy change for this reaction per mole of H2.
