Using the activity series (Table 4.5), write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (c) hydrobromic acid is added to tin metal

Using the activity series (Table 4.5), write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (a) Nickel metal is added to a solution of copper(II) nitrate
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Activity Series
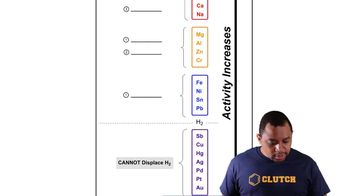
Single Replacement Reaction

Balancing Chemical Equations

Using the activity series (Table 4.5), write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (d) hydrogen gas is bubbled through an aqueous solution of nickel(II) chloride
Using the activity series (Table 4.5), write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (e) aluminum metal is added to a solution of cobalt(II) sulfate.
Using the activity series (Table 4.5), write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (b) a solution of zinc nitrate is added to a solution of magnesium sulfate (c) hydrochloric acid is added to gold metal
Using the activity series (Table 4.5), write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (d) chromium metal is immersed in an aqueous solution of cobalt(II) chloride
Using the activity series (Table 4.5), write balanced chemical equations for the following reactions. If no reaction occurs, write NR. (e) hydrogen gas is bubbled through a solution of silver nitrate.
