You are titrating an acidic solution with a basic one, and just realized you forgot to add the indicator that tells you when the equivalence point is reached. In this titration, the indicator turns blue at the equivalence point from an initially colorless solution. You quickly grab a bottle of indicator and add some to your titration beaker, and the whole solution turns dark blue. What do you do now?
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 4, Problem 13b
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (b) If you add a nonelectrolyte to an aqueous solution that already contains an electrolyte, the electrical conductivity will not change.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the concept of electrolytes and nonelectrolytes: Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions in solution, allowing the solution to conduct electricity. Nonelectrolytes do not dissociate into ions and therefore do not contribute to electrical conductivity.
Consider the effect of adding a nonelectrolyte to a solution: When a nonelectrolyte is added to a solution, it does not produce ions. Therefore, it does not increase the number of charge carriers in the solution.
Analyze the impact on electrical conductivity: Since the nonelectrolyte does not increase the number of ions, it does not enhance the solution's ability to conduct electricity. The existing ions from the electrolyte remain the only contributors to conductivity.
Evaluate the statement: The statement claims that adding a nonelectrolyte to a solution with an electrolyte will not change the electrical conductivity. Based on the analysis, this is true because the nonelectrolyte does not affect the ion concentration.
Justify the conclusion: The electrical conductivity of a solution depends on the presence of ions. Since nonelectrolytes do not provide additional ions, the conductivity remains unchanged when they are added to a solution already containing an electrolyte.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrolytes and Nonelectrolytes
Electrolytes are substances that dissociate into ions when dissolved in water, allowing the solution to conduct electricity. Nonelectrolytes, on the other hand, do not dissociate into ions and therefore do not contribute to electrical conductivity. Understanding the difference between these two types of substances is crucial for analyzing their effects on conductivity in a solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
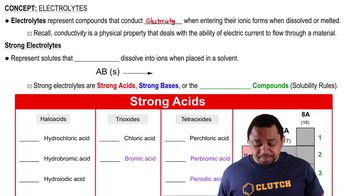
Electrolytes and Strong Acids
Electrical Conductivity
Electrical conductivity is a measure of a solution's ability to conduct electric current, which depends on the concentration and mobility of ions present in the solution. When electrolytes are dissolved in water, they increase the number of free ions, enhancing conductivity. The addition of a nonelectrolyte does not introduce any new ions, which is key to understanding how conductivity is affected.
Recommended video:
Guided course
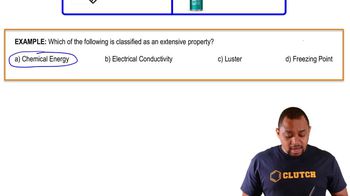
Extensive Property Example
Concentration and Ion Contribution
The overall conductivity of a solution is influenced by the concentration of ions present. When a nonelectrolyte is added to a solution containing an electrolyte, it does not change the number of ions, thus maintaining the same level of conductivity. This concept is essential for justifying whether the statement about conductivity changes is true or false.
Recommended video:
Guided course
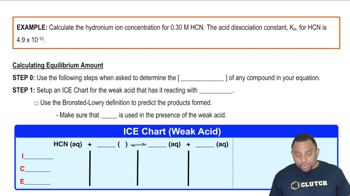
Hydronium Ion Concentration Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(a) Do colloids made only of gases exist? Why or why not?
5
views
Textbook Question
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (a) Electrolyte solutions conduct electricity because electrons are moving through the solution.
Textbook Question
(b) In the 1850s, Michael Faraday prepared ruby-red
colloids of gold nanoparticles in water that are still stable
today. These brightly colored colloids look like solutions.
What experiment(s) could you do to determine whether a
given colored preparation is a solution or colloid?
Textbook Question
Choose the best answer: A colloidal dispersion of one liquid
in another is called (a) a gel, (b) an emulsion, (c) a foam,
(d) an aerosol
1
views
