Textbook Question
Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions that occur in each of the following cases. Identify the spectator ion or ions in each reaction.
(a) Ba(OH)2(aq) + FeCl3(aq) →
(b) ZnCl2(aq) + Cs2CO3(aq) →

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

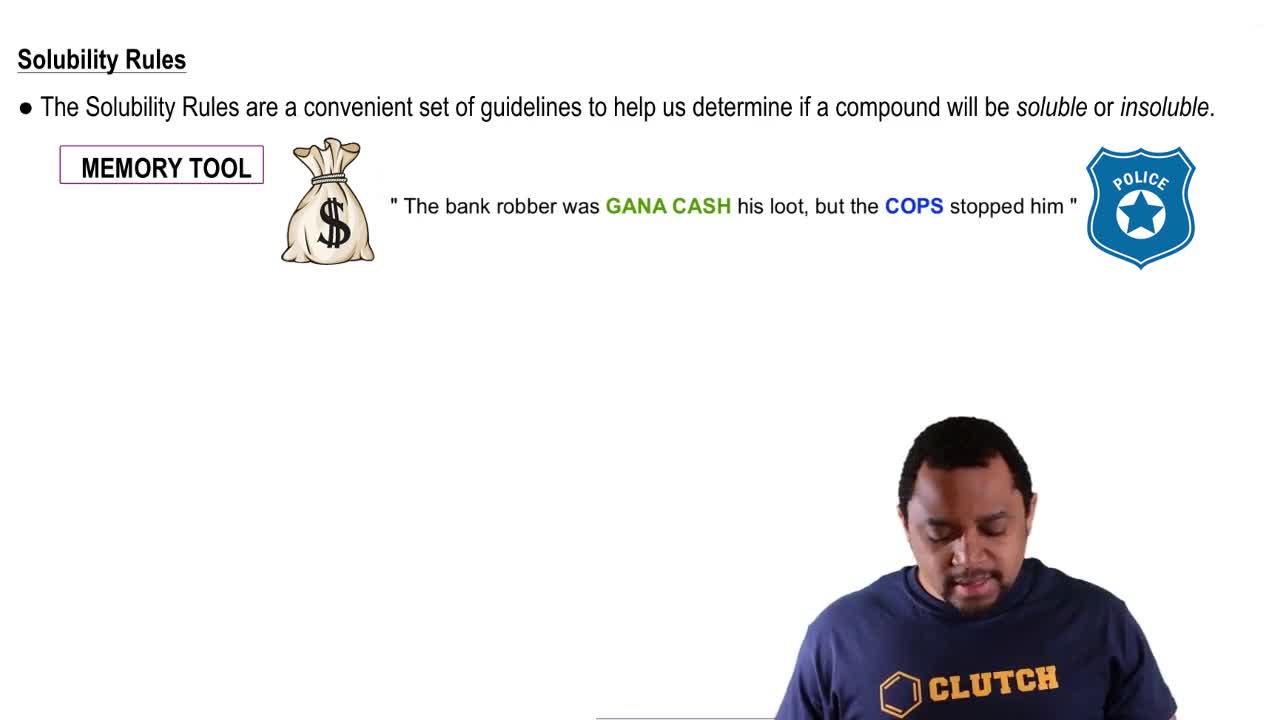

Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions that occur in each of the following cases. Identify the spectator ion or ions in each reaction.
(a) Ba(OH)2(aq) + FeCl3(aq) →
(b) ZnCl2(aq) + Cs2CO3(aq) →
Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions that occur in each of the following cases. Identify the spectator ion or ions in each reaction. (c) Na2S(aq) + CoSO4(aq) →
Three solutions are mixed together to form a single solution; in the final solution, there are 0.2 mol Pb1CH3COO)2, 0.1 mol Na2S, and 0.1 mol CaCl2 present. What solid(s) will precipitate?
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (a) Sulfuric acid is a monoprotic acid.