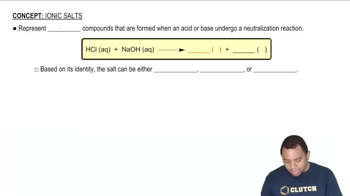
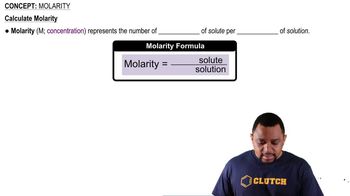
Textbook Question
You are presented with a white solid and told that due to careless labeling it is not clear if the substance is barium chloride, lead chloride, or zinc chloride. When you transfer the solid to a beaker and add water, the solid dissolves to give a clear solution. Next an Na2SO41aq2 solution is added and a white precipitate forms. What is the identity of the unknown white solid?
5
views