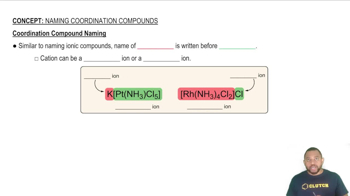
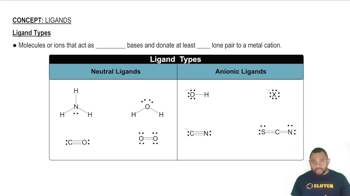
Four-coordinate metals can have either a tetrahedral or a square-planar geometry; both possibilities are shown here for [PtCl2(NH3)2].
a. What is the name of this molecule?
b. Would the tetrahedral molecule have a geometric isomer?
c. Would the tetrahedral molecule be diamagnetic or paramagnetic?
d. Would the square-planar molecule have a geometric isomer?