Ch.22 - Chemistry of the Nonmetals

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 22, Problem 49
Complete the exercises below. Write the chemical formula for each of the following compounds, and indicate the oxidation state of nitrogen in each: a. sodium nitrite, b. ammonia, c. nitrous oxide, d. sodium cyanide, e. nitric acid, f. nitrogen dioxide, g. nitrogen, h. boron nitride.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the chemical formula for each compound by using known chemical nomenclature rules: a. Sodium nitrite is NaNO_2, b. Ammonia is NH_3, c. Nitrous oxide is N_2O, d. Sodium cyanide is NaCN, e. Nitric acid is HNO_3, f. Nitrogen dioxide is NO_2, g. Nitrogen is N_2, h. Boron nitride is BN.
Determine the oxidation state of nitrogen in each compound by using the rules for assigning oxidation states: a. In NaNO_2, assign oxidation states to Na (+1) and O (-2) to find N, b. In NH_3, assign oxidation state to H (+1) to find N, c. In N_2O, use the fact that the sum of oxidation states must equal zero, d. In NaCN, assign oxidation states to Na (+1) and C (-4) to find N, e. In HNO_3, assign oxidation states to H (+1) and O (-2) to find N, f. In NO_2, assign oxidation state to O (-2) to find N, g. In N_2, use the fact that the molecule is diatomic and neutral, h. In BN, use the fact that B is typically +3 to find N.
For each compound, calculate the oxidation state of nitrogen by solving the equations set up in the previous step.
Verify the calculated oxidation states by ensuring that the sum of oxidation states in each compound equals the overall charge of the compound.
Review the oxidation states to ensure they are consistent with common oxidation states of nitrogen, which typically range from -3 to +5.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation State
The oxidation state, or oxidation number, is a concept used to indicate the degree of oxidation of an atom in a compound. It represents the hypothetical charge an atom would have if all bonds were ionic. Understanding oxidation states is crucial for determining how electrons are transferred in chemical reactions and for identifying the roles of different elements in compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Numbers
Chemical Formulas
A chemical formula is a symbolic representation of a compound that indicates the types and numbers of atoms present. It provides essential information about the composition of the substance, including the ratio of different elements. Writing accurate chemical formulas is fundamental in chemistry as it allows for the communication of chemical identities and stoichiometry in reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
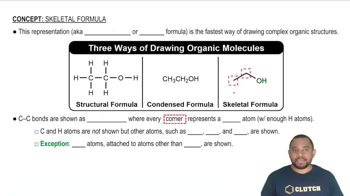
Skeletal Formula
Nitrogen Compounds
Nitrogen compounds encompass a wide range of substances that contain nitrogen in various oxidation states. These compounds exhibit diverse chemical behaviors and applications, from fertilizers to explosives. Familiarity with common nitrogen compounds, such as ammonia and nitric acid, is essential for understanding their properties, uses, and the role of nitrogen in biological and environmental systems.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Nitrogen Family Reactions
Related Practice
