Ch.22 - Chemistry of the Nonmetals

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 22, Problem 81
Complete the exercises below. Write a balanced equation for the reaction of each of the following compounds with water: f. Mg₃N₂ (s).
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the reactants and products. The compound given is magnesium nitride (Mg₃N₂), which reacts with water (H₂O). The products of this reaction are magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)₂) and ammonia (NH₃).
Step 2: Write the unbalanced chemical equation for the reaction. Start by writing the reactants and products: Mg₃N₂ (s) + H₂O (l) → Mg(OH)₂ (s) + NH₃ (g).
Step 3: Balance the magnesium atoms. There are 3 magnesium atoms in Mg₃N₂, so you need 3 Mg(OH)₂ on the product side: Mg₃N₂ (s) + H₂O (l) → 3 Mg(OH)₂ (s) + NH₃ (g).
Step 4: Balance the nitrogen atoms. There are 2 nitrogen atoms in Mg₃N₂, so you need 2 NH₃ on the product side: Mg₃N₂ (s) + H₂O (l) → 3 Mg(OH)₂ (s) + 2 NH₃ (g).
Step 5: Balance the hydrogen and oxygen atoms. Count the total number of hydrogen and oxygen atoms on both sides and adjust the number of water molecules accordingly to ensure both sides are balanced.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydrolysis Reaction
A hydrolysis reaction involves the reaction of a compound with water, resulting in the breakdown of that compound. In the case of metal nitrides like Mg₃N₂, hydrolysis leads to the formation of metal hydroxides and ammonia. Understanding this process is crucial for predicting the products of the reaction with water.
Recommended video:
Guided course
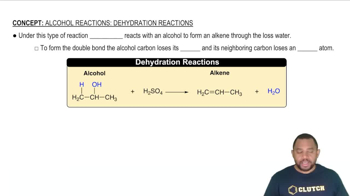
Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations is essential to ensure that the law of conservation of mass is upheld, meaning the number of atoms of each element must be the same on both sides of the equation. This involves adjusting coefficients in front of compounds to achieve balance. Mastery of this skill is necessary for accurately representing chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Balancing Chemical Equations
Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the quantitative relationship between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. It allows chemists to calculate the amounts of substances consumed and produced in a reaction. In the context of the given question, stoichiometry helps determine the correct ratios of magnesium hydroxide and ammonia produced from the hydrolysis of Mg₃N₂.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Stoichiometry Concept
Related Practice
