Textbook Question
Write a balanced equation for each of the following reactions:
a. Diborane reacts with water to form boric acid and molecular hydrogen.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance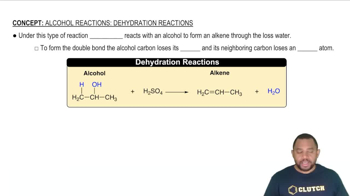


Write a balanced equation for each of the following reactions:
a. Diborane reacts with water to form boric acid and molecular hydrogen.
Write a balanced equation for each of the following reactions:
b. Upon heating, boric acid undergoes a condensation reaction to form tetraboric acid.
Write a balanced equation for each of the following reactions:
c. Boron oxide dissolves in water to give a solution of boric acid.