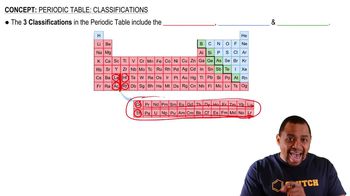
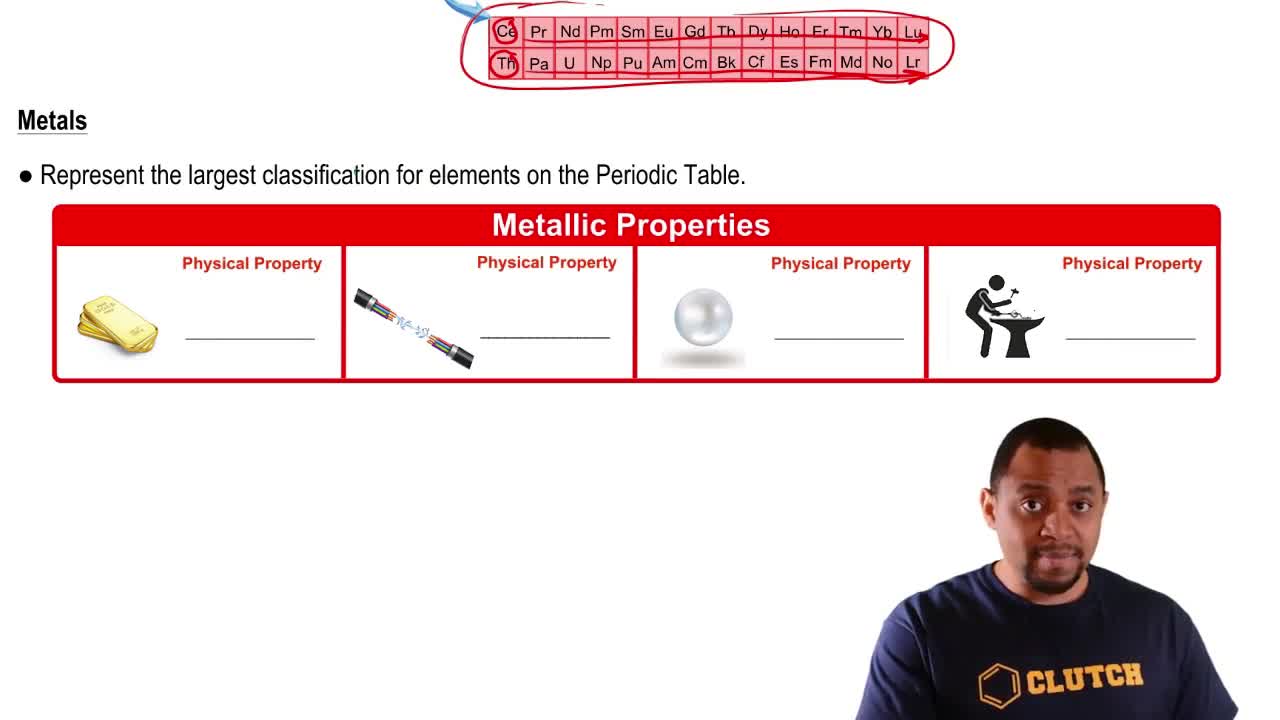
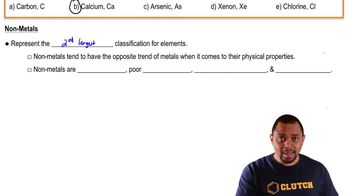
Textbook Question
Which property of the third-row nonmetallic elements might be the one depicted below:
a. first ionization energy,
b. atomic radius,
c. electronegativity,
d. melting point,
e. X―X single-bond enthalpy? [Find more in Sections 22.3, 22.4, 22.6, 22.8, and 22.10]