Ch.22 - Chemistry of the Nonmetals

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 22, Problem 64
Complete the exercises below. Give the chemical formula for: a. carbonic acid, b. sodium cyanide, c. potassium hydrogen carbonate, d. acetylene, e. iron pentacarbonyl.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the chemical formula for carbonic acid. Carbonic acid is formed from carbon dioxide and water, and its chemical formula is H2CO3.
Determine the chemical formula for sodium cyanide. Sodium cyanide is composed of sodium (Na) and the cyanide ion (CN^-), resulting in the formula NaCN.
Find the chemical formula for potassium hydrogen carbonate. Potassium hydrogen carbonate, also known as potassium bicarbonate, consists of potassium (K), hydrogen (H), and carbonate (CO3^2-), leading to the formula KHCO3.
Identify the chemical formula for acetylene. Acetylene is a simple alkyne hydrocarbon with the formula C2H2.
Determine the chemical formula for iron pentacarbonyl. Iron pentacarbonyl is a metal carbonyl compound with the formula Fe(CO)5, where iron is bonded to five carbon monoxide ligands.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Chemical Nomenclature
Chemical nomenclature is the system of naming chemical compounds based on their composition and structure. It follows specific rules set by organizations like IUPAC, which help in identifying the elements present and their arrangement. Understanding nomenclature is essential for translating names into chemical formulas and vice versa.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Properties
Acids and Bases
Acids are substances that can donate protons (H+) in a solution, while bases can accept protons. Carbonic acid, for example, is a weak acid formed from carbon dioxide and water. Recognizing the properties of acids and bases is crucial for identifying their chemical formulas and understanding their behavior in reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
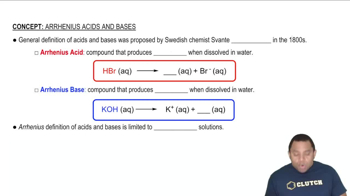
Arrhenius Acids and Bases
Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds consist of a central metal atom bonded to surrounding molecules or ions called ligands. Iron pentacarbonyl is an example where iron is coordinated to five carbon monoxide ligands. Understanding the structure and bonding in coordination compounds is important for writing their chemical formulas accurately.
Recommended video:
Guided course
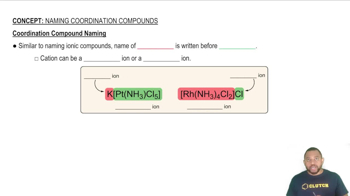
Coordination Compound Naming
Related Practice
