Textbook Question
Write balanced nuclear equations for the following transformations: (a) bismuth-213 undergoes alpha decay.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
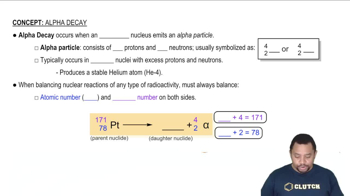
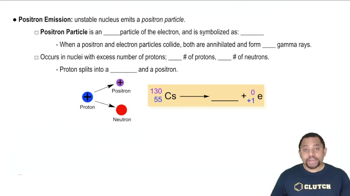

Write balanced nuclear equations for the following transformations: (a) bismuth-213 undergoes alpha decay.
Write balanced nuclear equations for the following transformations:
(b) nitrogen-13 undergoes electron capture.
Write balanced nuclear equations for the following transformations: (c) technicium-98 undergoes electron capture.
Decay of which nucleus will lead to the following products: (a) bismuth-211 by beta decay?
Decay of which nucleus will lead to the following products: (b) chromium-50 by positron emission?