Textbook Question
Each of the following transmutations produces a radionuclide used in positron emission tomography (PET).
(a) In equations (i) and (ii), identify the species signified as 'X.'
(i) 14N(p,α)X
(ii) 18O(p,X)18F
(iii) 14N(d,n)15O

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance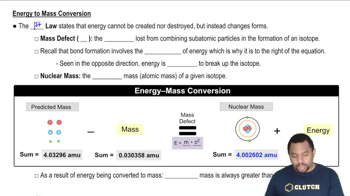

Each of the following transmutations produces a radionuclide used in positron emission tomography (PET).
(a) In equations (i) and (ii), identify the species signified as 'X.'
(i) 14N(p,α)X
(ii) 18O(p,X)18F
(iii) 14N(d,n)15O
The nuclear masses of 7Be, 9Be, and 10Be are 7.0147, 9.0100, and 10.0113 amu, respectively. Which of these nuclei has the largest binding energy per nucleon?