Textbook Question
Which are classified as ionizing radiation: X rays, alpha particles, microwaves from a cell phone, and gamma rays?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance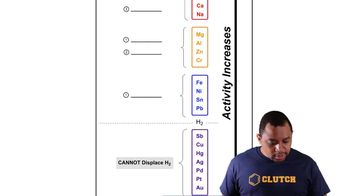
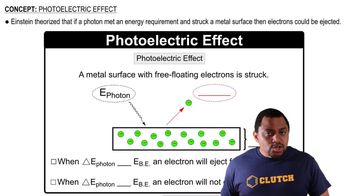

Which are classified as ionizing radiation: X rays, alpha particles, microwaves from a cell phone, and gamma rays?
A laboratory rat is exposed to an alpha-radiation source whose activity is 14.3 mCi. (a) What is the activity of the radiation in disintegrations per second? In becquerels?
A laboratory rat is exposed to an alpha-radiation source whose activity is 14.3 mCi. (b) The rat has a mass of 385 g and is exposed to the radiation for 14.0 s, absorbing 35% of the emitted alpha particles, each having an energy of 9.12 * 10-13 J. Calculate the absorbed dose in millirads and grays.
The table to the right gives the number of protons (p) and neutrons (n) for four isotopes. (a) Write the symbol for each of the isotopes.