In some applications nickel–cadmium batteries have been replaced by nickel–zinc batteries. The overall cell reaction for this relatively new battery is: 2 H2O(l) + 2 NiO(OH)(s) + Zn(s) → 2 Ni(OH)2(s) + Zn(OH)2(s) (c) A single nickel–cadmium cell has a voltage of 1.30 V. Based on the difference in the standard reduction potentials of Cd2+ and Zn2+, what voltage would you estimate a nickel–zinc battery will produce? (d) Would you expect the specific energy density of a nickel–zinc battery to be higher or lower than that of a nickel–cadmium battery?

Li-ion batteries used in automobiles typically use a LiMn2O4 cathode in place of the LiCoO2 cathode found in most Li-ion batteries. (b) Which material has a higher percentage of lithium? Does this help to explain why batteries made with LiMn2O4 cathodes deliver less power on discharging?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Lithium Content in Cathodes

Battery Power Delivery
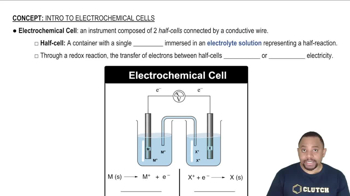
Electrochemical Properties of Cathode Materials
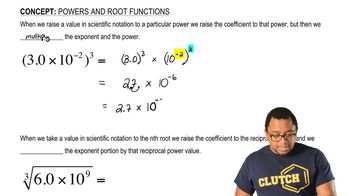
Li-ion batteries used in automobiles typically use a LiMn2O4 cathode in place of the LiCoO2 cathode found in most Li-ion batteries. (a) Calculate the mass percent lithium in each electrode material.
Li-ion batteries used in automobiles typically use a LiMn2O4 cathode in place of the LiCoO2 cathode found in most Li-ion batteries. (c) In a battery that uses a LiCoO2 cathode, approximately 50% of the lithium migrates from the cathode to the anode on charging. In a battery that uses a LiMn2O4 cathode, what fraction of the lithium in LiMn2O4 would need to migrate out of the cathode to deliver the same amount of lithium to the graphite anode?
(a) Which reaction is spontaneous in the hydrogen fuel cell: hydrogen gas plus oxygen gas makes water, or water makes hydrogen gas plus oxygen gas?
