Consider the following organic substances: ethylethanoate, ethylmethylether, hexanol, and propanone. (a) Which of these molecules contains three carbons?

Chloropropane is derived from propane by substituting Cl for H on one of the carbon atoms. (b) Suggest names for these two compounds.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
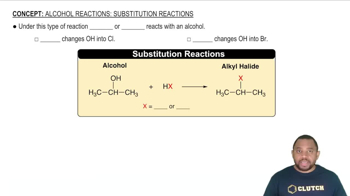
Substitution Reactions
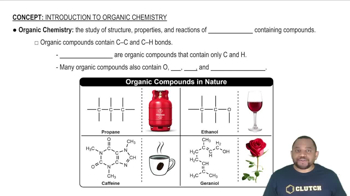
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
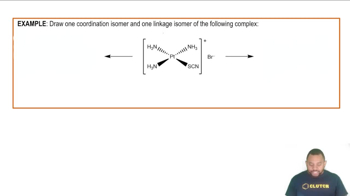
Isomerism
Consider the following organic substances: ethylethanoate, ethylmethylether, hexanol, and propanone. (b) Which of these molecules contain a C = O group?
Chloropropane is derived from propane by substituting Cl for H on one of the carbon atoms. (a) Draw the structural formulas for the two isomers of chloropropane.
Suppose a scientist repeats the Millikan oil-drop experiment but reports the charges on the drops using an unusual (and imaginary) unit called the warmomb (wa). The scientist obtains the following data for four of the drops: Droplet Calculated Charge (wa) A 3.84⨉10−8 B 4.80⨉10−8 C 2.88⨉10−8 D 8.64⨉10−8 (a) If all the droplets were the same size, which would fall most slowly through the apparatus?
Suppose a scientist repeats the Millikan oil-drop experiment but reports the charges on the drops using an unusual (and imaginary) unit called the warmomb (wa). The scientist obtains the following data for four of the drops: Droplet Calculated Charge (wa) A 3.84⨉10−8 B 4.80⨉10−8 C 2.88⨉10−8 D 8.64⨉10−8 (b) From these data, what is the best choice for the charge of the electron in warmombs?
