Textbook Question
(b) Among the four alkanes, ethane, propane, butane, and pentane, which is capable of existing in isomeric forms?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
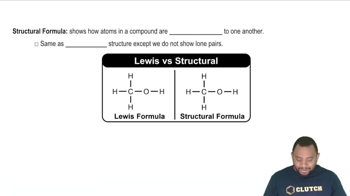

(b) Among the four alkanes, ethane, propane, butane, and pentane, which is capable of existing in isomeric forms?
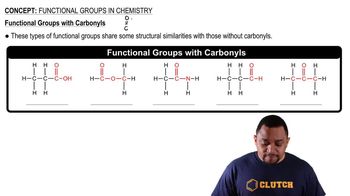
(a) What is a functional group?
(b) What functional group characterizes an alcohol?
Consider the following organic substances: ethylethanoate, ethylmethylether, hexanol, and propanone. (a) Which of these molecules contains three carbons?
Consider the following organic substances: ethylethanoate, ethylmethylether, hexanol, and propanone. (b) Which of these molecules contain a C = O group?
Chloropropane is derived from propane by substituting Cl for H on one of the carbon atoms. (a) Draw the structural formulas for the two isomers of chloropropane.