Textbook Question
(a) What is the difference between a state and a microstate of a system?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
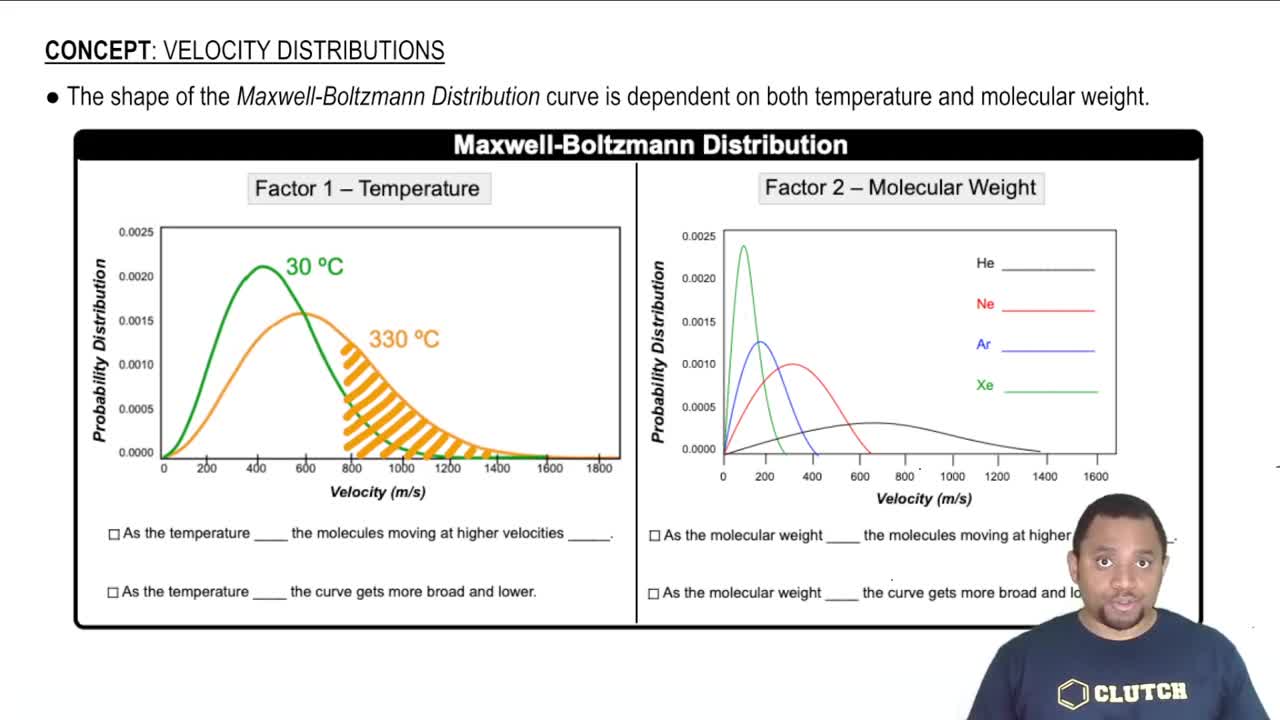
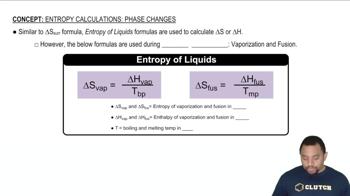
(a) What is the difference between a state and a microstate of a system?
(b) As a system goes from state A to state B, its entropy decreases. What can you say about the number of microstates corresponding to each state?
(c) In a particular spontaneous process, the number of microstates available to the system decreases. What can you conclude about the sign of ΔSsurr?
Would each of the following changes increase, decrease, or have no effect on the number of microstates available to a system: (b) decrease in volume