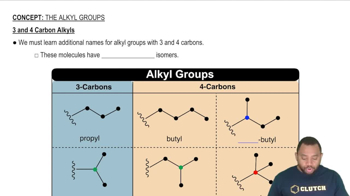
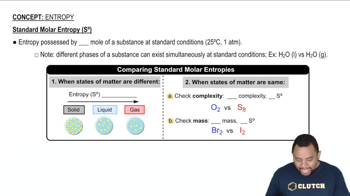
Textbook Question
The standard entropies at 298 K for certain group 4A elements are: C(s, diamond) = 2.43 J>mol@K, Si1s2 = 18.81 J>mol@K, Ge1s2 = 31.09 J>mol@K, and Sn1s2 = 51.818 J>mol@K. All but Sn have the same (diamond) structure. How do you account for the trend in the S° values?