The normal boiling point of Br2(l) is 58.8 °C, and its molar enthalpy of vaporization is ΔHvap = 29.6 kJ/mol. (a) When Br2(l) boils at its normal boiling point, does its entropy increase or decrease?
Ch.19 - Chemical Thermodynamics

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 19, Problem 24a
The element gallium (Ga) freezes at 29.8 °C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is ΔHfus = 5.59 kJ/mol. (a) When molten gallium solidifies to Ga(s) at its normal melting point, is ΔS positive or negative?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Start by understanding the process: When molten gallium solidifies, it changes from a liquid to a solid state.
Recall that entropy (ΔS) is a measure of disorder or randomness in a system.
In general, the entropy of a solid is lower than that of a liquid because the particles in a solid are more ordered.
Since the process involves going from a more disordered state (liquid) to a more ordered state (solid), the change in entropy (ΔS) is expected to be negative.
Therefore, when molten gallium solidifies, ΔS is negative because the system becomes more ordered.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
51sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Entropy (ΔS)
Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a system. In thermodynamics, a positive change in entropy (ΔS > 0) indicates an increase in disorder, while a negative change (ΔS < 0) signifies a decrease in disorder. When a substance transitions from a liquid to a solid, such as gallium solidifying, the molecules become more ordered, leading to a negative change in entropy.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Entropy in Thermodynamics
Phase Changes
Phase changes refer to the transitions between different states of matter, such as solid, liquid, and gas. During these transitions, energy is either absorbed or released, affecting the system's enthalpy and entropy. In the case of gallium, when it freezes at its melting point, it releases energy (enthalpy of fusion), which is crucial for understanding the thermodynamic behavior of the substance during solidification.
Recommended video:
Guided course
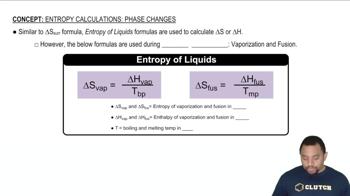
Entropy in Phase Changes
Enthalpy of Fusion (ΔH<sub>fus</sub>)
The enthalpy of fusion is the amount of energy required to change a substance from solid to liquid at its melting point, or vice versa. For gallium, the enthalpy of fusion is 5.59 kJ/mol, indicating the energy released when it solidifies. This energy change is important for determining the thermodynamic properties of the phase transition and its impact on entropy.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Enthalpy of Formation Example 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
The normal boiling point of Br2(𝑙) is 58.8 °C, and its molar enthalpy of vaporization is Δ𝐻vap=29.6kJ/mol. (b) Calculate the value of Δ𝑆 when 1.00 mol of Br2(𝑙) is vaporized at 58.8 °C.
Textbook Question
The element gallium (Ga) freezes at 29.8 °C, and its molar enthalpy of fusion is ΔHfus = 5.59 kJ/mol. (b) Calculate the value of ΔS when 60.0 g of Ga(l) solidifies at 29.8 °C.
Textbook Question
Indicate whether each statement is true or false. (c) In a certain spontaneous process the system undergoes an entropy change of 4.2 J/K; therefore, the entropy change of the surroundings must be -4.2 J/K.
Textbook Question
(a) Does the entropy of the surroundings increase for spontaneous processes?
