(a) Which of the thermodynamic quantities T, E, q, w, and S are state functions? (b) Which depend on the path taken from one state to another?

The crystalline hydrate Cd(NO3)2⋅4 H2O(s) loses water when placed in a large, closed, dry vessel at room temperature: Cd(NO3)2⋅4 H2O(s) → Cd(NO3)2(s) + 4 H2O(g) This process is spontaneous and ΔH° is positive at room temperature.
(a) What is the sign of ΔS° at room temperature?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Entropy (ΔS)

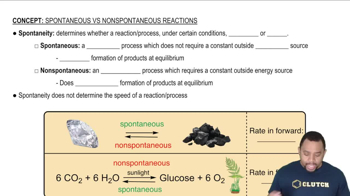
Spontaneity of Reactions
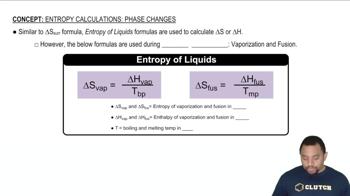
Phase Changes and Energy
(d) For a reversible isothermal process, write an expression for ΔE in terms of q and w and an expression for ΔS in terms of q and T.
The crystalline hydrate Cd(NO3)2⋅4 H2O(s) loses water when placed in a large, closed, dry vessel at room temperature: Cd(NO3)2⋅4 H2O(s) → Cd(NO3)2(s) + 4 H2O(g) This process is spontaneous and ΔH° is positive at room temperature.
(b) If the hydrated compound is placed in a large, closed vessel that already contains a large amount of water vapor, does ΔS° change for this reaction at room temperature?
For each of the following processes, indicate whether the signs of ΔS and ΔH are expected to be positive, negative, or about zero. (a) A solid sublimes. (b) The temperature of a sample of Co(s) is lowered from 60 °C to 25 °C. (c) Ethyl alcohol evaporates from a beaker. (d) A diatomic molecule dissociates into atoms. (e) A piece of charcoal is combusted to form CO2(g) and H2O(g).
