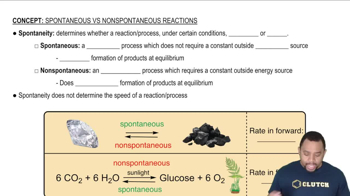
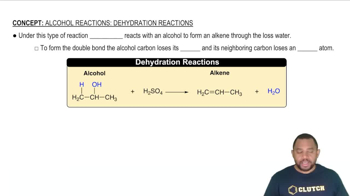
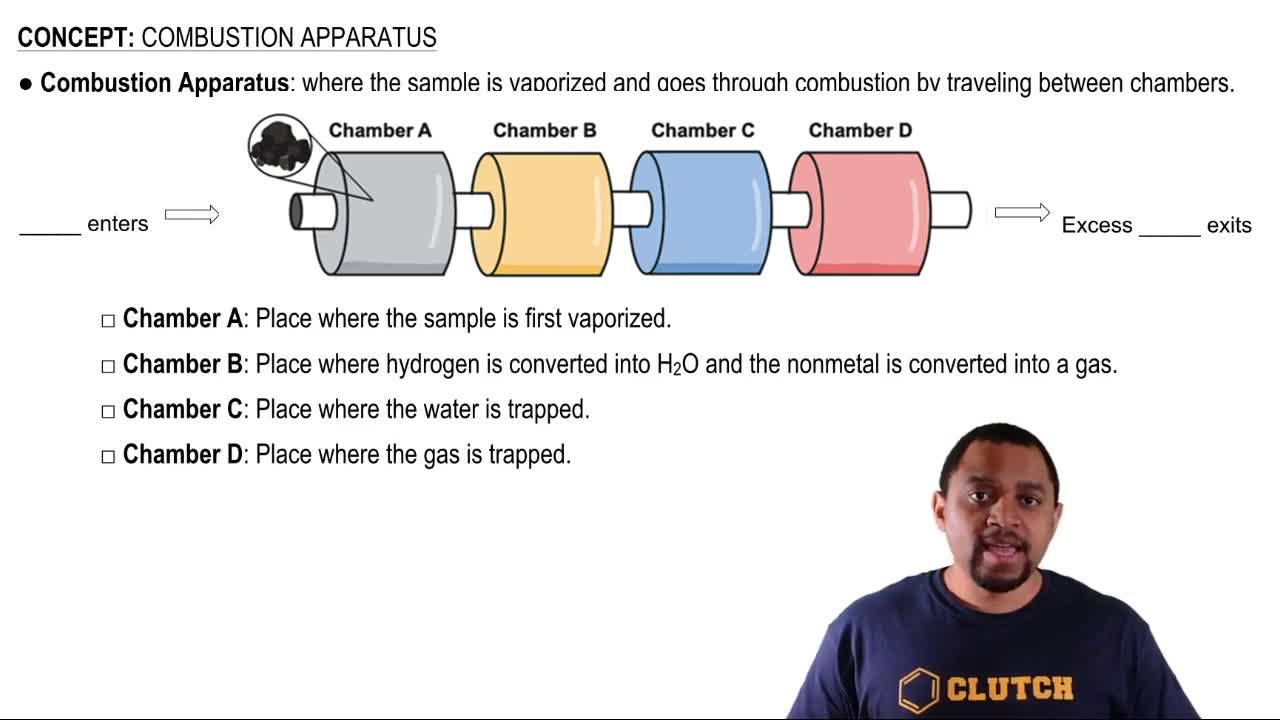
The oxidation of glucose (C6H12O6) in body tissue produces CO2 and H2O. In contrast, anaerobic decomposition, which occurs during fermentation, produces ethanol (C2H5OH) and CO2.
(b) Compare the maximum work that can be obtained from these processes under standard conditions.
C6H12O6(s) + 6 O2(g) ⇌ 6 CO2(g) + 6 H2O(l)
C6H12O6(s) ⇌ 2 C2H5OH(l) + 2 CO2(g)