Textbook Question
Predict the sign of ΔSsys for each of the following processes: (b) Gaseous Cl2 dissociates in the stratosphere to form gaseous Cl atoms.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance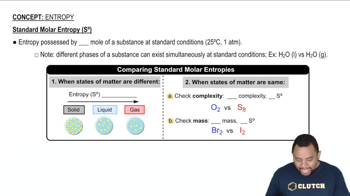
Predict the sign of ΔSsys for each of the following processes: (b) Gaseous Cl2 dissociates in the stratosphere to form gaseous Cl atoms.
Predict the sign of ΔSsys for each of the following processes: (c) Gaseous CO reacts with gaseous H2 to form liquid methanol, CH3OH.
Predict the sign of ΔSsys for each of the following processes: (d) Calcium phosphate precipitates upon mixing Ca(NO3)2(aq) and (NH4)3PO4(aq).
Cyclopropane and propylene are isomers that both have the formula C3H6. Based on the molecular structures shown, which of these isomers would you expect to have the higher standard molar entropy at 25 °C?