Textbook Question
(b) In a particular spontaneous process the entropy of the system decreases. What can you conclude about the sign and magnitude of ΔSsurr?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

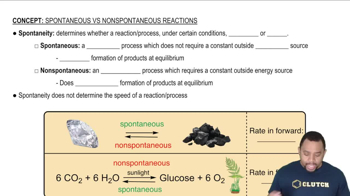
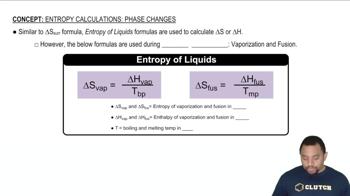
(b) In a particular spontaneous process the entropy of the system decreases. What can you conclude about the sign and magnitude of ΔSsurr?
(c) During a certain reversible process, the surroundings undergo an entropy change, ΔSsurr = -78 J/K. What is the entropy change of the system for this process?
For the isothermal expansion of a gas into a vacuum, ΔE = 0, q = 0, and w = 0. (b) Explain why no work is done by the system during this process.
(a) What is the difference between a state and a microstate of a system?