Textbook Question
Calculate the molar solubility of Ni(OH)2 when buffered at pH (a) 8.0.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
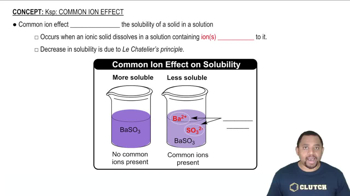

Calculate the molar solubility of Ni(OH)2 when buffered at pH (a) 8.0.
Calculate the molar solubility of Ni(OH)2 when buffered at pH (b) 10.0.
Calculate the molar solubility of Ni(OH)2 when buffered at pH (c) 12.0.
For each of the following slightly soluble salts, write the net ionic equation, if any, for reaction with a strong acid: (a) MnS (b) PbF2 (c) AuCl3 (e) CuBr (d) Hg2C2O4.
From the value of Kf listed in Table 17.1, calculate the concentration of Ni2 +1aq2 and Ni1NH326 2+ that are present at equilibrium after dissolving 1.25 g NiCl2 in 100.0 mL of 0.20 M NH31aq2.