(a) A 0.1044-g sample of an unknown monoprotic acid requires 22.10 mL of 0.0500 M NaOH to reach the end point. What is the molar mass of the unknown?
Ch.17 - Additional Aspects of Aqueous Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 17, Problem 114
What is the pH at 25 C of water saturated with CO2 at a partial pressure of 1.10 atm? The Henry's law constant for CO2 at 25 C is 3.1 * 10-2 mol>L@atm.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Use Henry's Law to calculate the concentration of CO2 in the water. Henry's Law states that the concentration of a gas in a liquid is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas above the liquid. The formula is: C = kP, where C is the concentration, k is the Henry's Law constant, and P is the partial pressure.
Step 2: Substitute the given values into the Henry's Law equation. The Henry's Law constant (k) for CO2 at 25 C is 3.1 * 10^-2 mol/L*atm and the partial pressure (P) is 1.10 atm.
Step 3: The CO2 in water will form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which is a weak acid. This will dissociate into H+ and HCO3- ions. Write the chemical equation for this reaction: CO2 + H2O -> H2CO3 -> H+ + HCO3-.
Step 4: Use the concentration of CO2 calculated in step 2 as the initial concentration of H2CO3. Since we are assuming that all the CO2 forms H2CO3, the initial concentration of H+ and HCO3- is zero.
Step 5: Use the definition of pH to calculate the pH of the solution. The pH is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the concentration of H+ ions in the solution. Since the concentration of H+ ions is equal to the concentration of H2CO3, you can use the concentration calculated in step 2 to find the pH.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
7mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and Acidity
pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution, indicating its acidity or basicity. A pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic. The pH scale is logarithmic, meaning each whole number change represents a tenfold change in hydrogen ion concentration.
Recommended video:
Guided course
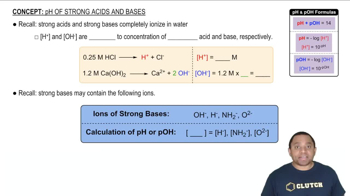
pH of Strong Acids and Bases
Henry's Law
Henry's Law states that the amount of gas that dissolves in a liquid at a given temperature is proportional to the partial pressure of that gas above the liquid. This relationship is expressed as C = kH * P, where C is the concentration of the gas in the liquid, kH is the Henry's law constant, and P is the partial pressure of the gas.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Henry's Law Calculations
Carbonic Acid Formation
When CO2 dissolves in water, it reacts to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which can dissociate into bicarbonate (HCO3-) and hydrogen ions (H+). This increase in hydrogen ions lowers the pH of the solution, making it more acidic. Understanding this reaction is crucial for calculating the pH of water saturated with CO2.
Recommended video:
Guided course
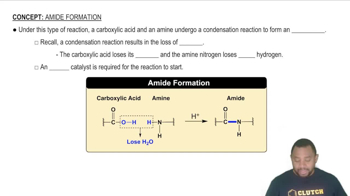
Amide Formation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(b) As the acid is titrated, the pH of the solution after the addition of 11.05 mL of the base is 4.89. What is the Ka for the acid?
Textbook Question
The osmotic pressure of a saturated solution of strontium sulfate at 25 C is 21 torr. What is the solubility product of this salt at 25 C?
Textbook Question
A concentration of 10–100 parts per billion (by mass) of Ag+ is an effective disinfectant in swimming pools. However, if the concentration exceeds this range, the Ag+ can cause adverse health effects. One way to maintain an appropriate concentration of Ag+ is to add a slightly soluble salt to the pool. Using Ksp values from Appendix D, calculate the equilibrium concentration of Ag+ in parts per billion that would exist in equilibrium with (b) AgBr (c) AgI.
