Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (b) calcium hydroxide titrated with perchloric acid.

Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (a) NaHCO3 titrated with NaOH (c) KOH titrated with HBr.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Acid-Base Titration
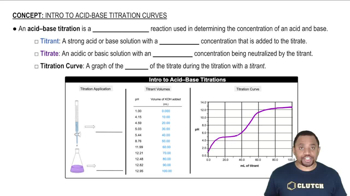
Equivalence Point and pH
Buffer Solutions

The samples of nitric and acetic acids shown here are both titrated with a 0.100 M solution of NaOH(aq).
Determine whether each of the following statements concerning these titrations is true or false. (a) A larger volume of NaOH1aq2 is needed to reach the equivalence point in the titration of HNO3.
Determine whether each of the following statements concerning the titrations in Problem 17.35 is true or false. (a) The pH at the beginning of the two titrations will be the same.
Determine whether each of the following statements concerning the titrations in Problem 17.35 is true or false. (b) The titration curves will both be essentially the same after passing the equivalence point.
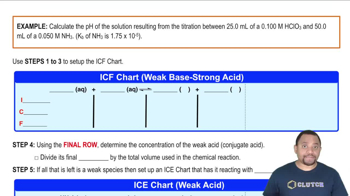
Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (b) NH3 titrated with HCl.
Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (a) formic acid titrated with NaOH.
