Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (b) calcium hydroxide titrated with perchloric acid.

Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (c) pyridine titrated with nitric acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Acid-Base Titration
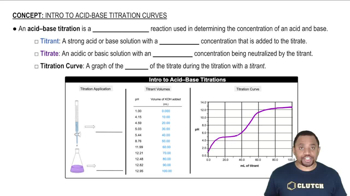
Strength of Acids and Bases

Equivalence Point and pH
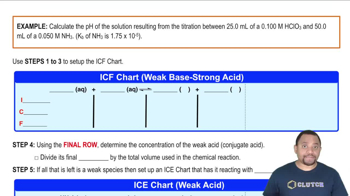
Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (b) NH3 titrated with HCl.
Predict whether the equivalence point of each of the following titrations is below, above, or at pH 7: (a) formic acid titrated with NaOH.
Assume that 30.0 mL of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base B that accepts one proton is titrated with a 0.10 M solution of the monoprotic strong acid HA. (a) How many moles of HA have been added at the equivalence point?
Assume that 30.0 mL of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base B that accepts one proton is titrated with a 0.10 M solution of the monoprotic strong acid HA. (b) What is the predominant form of B at the equivalence point?
Assume that 30.0 mL of a 0.10 M solution of a weak base B that accepts one proton is titrated with a 0.10 M solution of the monoprotic strong acid HA. (c) Is the pH 7, less than 7, or more than 7 at the equivalence point?
