Textbook Question
Calculate the minimum pH needed to precipitate Mn1OH22 so completely that the concentration of Mn2 +1aq2 is less than 1 mg per liter [1 part per billion (ppb)].

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
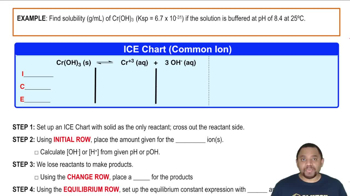

Calculate the minimum pH needed to precipitate Mn1OH22 so completely that the concentration of Mn2 +1aq2 is less than 1 mg per liter [1 part per billion (ppb)].
Suppose that a 10-mL sample of a solution is to be tested for I- ion by addition of 1 drop (0.2 mL) of 0.10 M Pb1NO322. What is the minimum number of grams of I- that must be present for PbI21s2 to form?