
The amino acid glycine H₂N¬CH₂¬COOH can participate in the following equilibria in water: H₂N¬CH₂¬COOH + H₂O ⇌ H₂N¬CH₂¬COO⁻ + H₃O⁺ with Ka = 4.3 × 10⁻³, and H₂N¬CH₂¬COOH + H₂O ⇌ +H₃N¬CH₂¬COOH + OH⁻ with Kb = 6.0 × 10⁻⁵. (c) What would be the predominant form of glycine in a solution with pH 13? With pH 1?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Acid-Base Equilibria
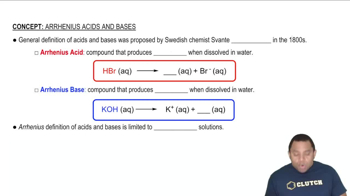
pH and Its Relation to Protonation States
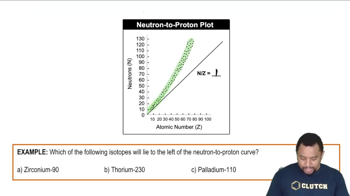
Zwitterions
The following observations are made about a diprotic acid H2A: (i) A 0.10 M solution of H2A has pH = 3.30. (ii) A 0.10 M solution of the salt NaHA is acidic. Which of the following could be the value of pKa2 for H2A: (i) 3.22, (ii) 5.30, (iii) 7.47, or (iv) 9.82?
The amino acid glycine (H2N–CH2–COOH) can participate in the following equilibria in water:
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O ⇌ H2N–CH2–COO– + H3O+ Ka = 4.3 × 10-3
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O⇌ +H3N–CH2–COOH + OH- Kb = 6.0 × 10-5
(a) Use the values of Ka and Kb to estimate the equilibrium constant for the intramolecular proton transfer to form a zwitterion: H2N–CH2–COOH ⇌ +H3N–CH2–COO–
The amino acid glycine (H2N–CH2–COOH) can participate in the following equilibria in water:
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O ⇌ H2N–CH2–COO– + H3O+ Ka = 4.3 × 10-3
H2N–CH2–COOH + H2O⇌ +H3N–CH2–COOH + OH- Kb = 6.0 × 10-5
(b) What is the pH of a 0.050 M aqueous solution of glycine?
