Textbook Question
Predict the products of the following acid–base reactions, and predict whether the equilibrium lies to the left or to the right of the reaction arrow:
(a) O2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌
(b) CH3COOH(aq) + HS-(aq) ⇌
(c) NO2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance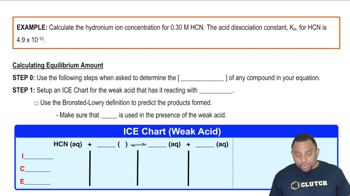
Predict the products of the following acid–base reactions, and predict whether the equilibrium lies to the left or to the right of the reaction arrow:
(a) O2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌
(b) CH3COOH(aq) + HS-(aq) ⇌
(c) NO2-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌
Predict the products of the following acid–base reactions, and predict whether the equilibrium lies to the left or to the right of the reaction arrow:
(a) NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq) ⇌
(b) CH3COO-(aq) + H3O+(aq) ⇌
(c) HCO3-(aq) + F-(aq) ⇌
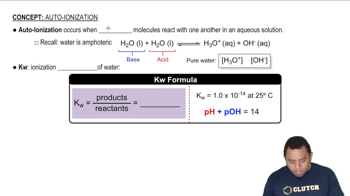
Write a chemical equation that illustrates the autoionization of water.
Write the expression for the ion product constant for water, Kw.