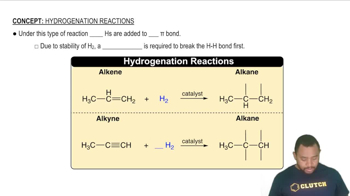
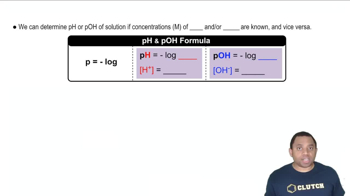
Textbook Question
Which of the following solutions is the most basic?(a) 0.6 M NaCl, (b) 0.150 M CsOH, (c) 0.100 M Sr1OH22.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Deuterium oxide 1D2O, where D is deuterium, the hydrogen-2 isotope) has an ion-product constant, Kw, of 8.9 * 10-16 at 20 °C. Calculate 3D+4 and 3OD-4 for pure (neutral) D2O at this temperature.
By what factor does [H+] change for a pH change of (a) 2.00 units? (b) 0.50 units?
The average pH of normal arterial blood is 7.40. At normal body temperature 137 °C2, Kw = 2.4 * 10-14. Calculate 3H+4, 3OH-4, and pOH for blood at this temperature.