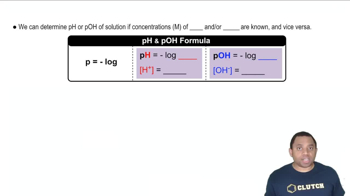
Textbook Question
Atmospheric CO2 levels have risen by nearly 20% over the past 40 years from 320 ppm to 400 ppm. (a) Given that the average pH of clean, unpolluted rain today is 5.4, determine the pH of unpolluted rain 40 years ago. Assume that carbonic acid 1H2CO32 formed by the reaction of CO2 and water is the only factor influencing pH. CO21g2 + H2O1l2 Δ H2CO31aq2