Textbook Question
Calculate [OH-] and pH for each of the following strong base solutions: (c) 10.0 mL of 0.0105 M Ca(OH)2 diluted to 500.0 mL

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
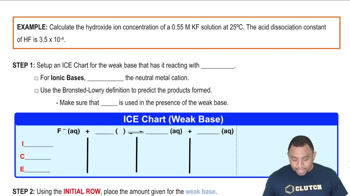

Calculate [OH-] and pH for each of the following strong base solutions: (c) 10.0 mL of 0.0105 M Ca(OH)2 diluted to 500.0 mL
Calculate the concentration of an aqueous solution of Ca1OH22 that has a pH of 10.05.
Write the chemical equation and the Ka expression for the acid dissociation of each of the following acids in aqueous solution. First show the reaction with H+(a)q as a product and then with the hydronium ion: (a) C6H5COOH (b) HCO3-