Textbook Question
Butyric acid is responsible for the foul smell of rancid butter. The pKa of butyric acid is 4.84. (a) Calculate the pKb for the butyrate ion.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
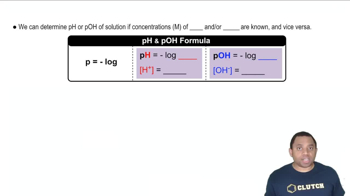


Butyric acid is responsible for the foul smell of rancid butter. The pKa of butyric acid is 4.84. (a) Calculate the pKb for the butyrate ion.
Butyric acid is responsible for the foul smell of rancid butter. The pKa of butyric acid is 4.84. (b) Calculate the pH of a 0.050 M solution of butyric acid.
Arrange the following 0.10 M solutions in order of increasing acidity: (i) NH4NO3, (ii) NaNO3, (iii) CH3COONH4, (iv) NaF, (v) CH3COONa.
The following observations are made about a diprotic acid H2A: (i) A 0.10 M solution of H2A has pH = 3.30. (ii) A 0.10 M solution of the salt NaHA is acidic. Which of the following could be the value of pKa2 for H2A: (i) 3.22, (ii) 5.30, (iii) 7.47, or (iv) 9.82?