Textbook Question
An unknown salt is either KBr, NH4Cl, KCN, or K2CO3. If a 0.100 M solution of the salt is neutral, what is the identity of the salt?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
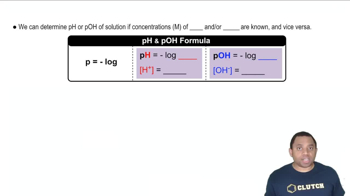
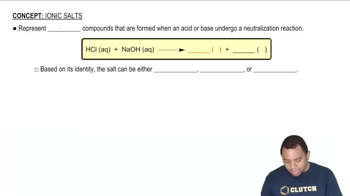

An unknown salt is either KBr, NH4Cl, KCN, or K2CO3. If a 0.100 M solution of the salt is neutral, what is the identity of the salt?
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following substances are acidic, basic, or neutral: (c) NaClO
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following substances are acidic, basic, or neutral: (d) 3CH3NH34NO3
Predict whether aqueous solutions of the following substances are acidic, basic, or neutral: (e) Na2SO3.