The indicator methyl orange has been added to both of the following solutions. Based on the colors, classify each statement as true or false: (a) The pH of solution A is definitely less than 7.00. (b) The pH of solution B is definitely greater than 7.00. (c) The pH of solution B is greater than that of solution A.
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 4
Addition of phenolphthalein to an unknown colorless solution does not cause a color change. The addition of bromthymol blue to the same solution leads to a yellow color. (a) Is the solution acidic, neutral, or basic?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the role of indicators: Phenolphthalein and bromthymol blue are pH indicators that change color at specific pH ranges. Phenolphthalein is colorless in acidic to neutral solutions and turns pink in basic solutions (pH > 8.2). Bromthymol blue is yellow in acidic solutions (pH < 6.0), green in neutral solutions, and blue in basic solutions (pH > 7.6).
Analyze the effect of phenolphthalein: Since the addition of phenolphthalein to the solution does not cause a color change, the solution is not basic. This means the pH is likely below 8.2.
Analyze the effect of bromthymol blue: The addition of bromthymol blue results in a yellow color, indicating that the solution is acidic, as bromthymol blue is yellow at pH values below 6.0.
Combine the observations: The lack of color change with phenolphthalein and the yellow color with bromthymol blue both suggest that the solution is acidic.
Conclude the solution's nature: Based on the behavior of both indicators, the solution is acidic.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH Indicators
pH indicators are substances that change color in response to changes in pH levels. Phenolphthalein is colorless in acidic and neutral solutions but turns pink in basic solutions, while bromthymol blue is yellow in acidic conditions and blue in basic conditions. Understanding how these indicators function helps determine the acidity or basicity of a solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
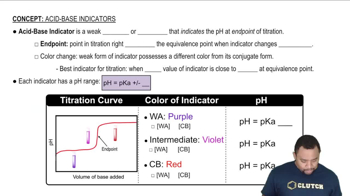
Acid-Base Indicators
Acid-Base Theory
Acid-base theory explains the behavior of acids and bases in terms of proton (H+) transfer. According to the Brønsted-Lowry theory, acids donate protons while bases accept them. The color change observed with bromthymol blue indicates that the solution is acidic, as it turns yellow in the presence of excess H+ ions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Bronsted-Lowry Acid-Base Theory
pH Scale
The pH scale quantifies the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 (very acidic) to 14 (very basic), with 7 being neutral. A pH less than 7 indicates an acidic solution, while a pH greater than 7 indicates a basic solution. The behavior of the indicators in the unknown solution suggests that its pH is below 7, confirming its acidic nature.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The pH Scale
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
The probe of the pH meter shown here is sitting in a beaker that contains a clear liquid. You are told the liquid is pure water, a solution of HCl(aq), or a solution of KOH(aq). (b) If the liquid is one of the solutions, what is its molarity?
Textbook Question
The probe of the pH meter shown here is sitting in a beaker that contains a clear liquid. (c) Why is the temperature given on the pH meter?
Textbook Question
The following diagrams represent aqueous solutions of three acids, HX, HY, and HZ. The water molecules have been omitted for clarity, and the hydrated proton is represented as H+ rather than H3O+. (a) Which of the acids is a strong acid? Explain.
