Phenylacetic acid 1C6H5CH2COOH2 is one of the substances that accumulates in the blood of people with phenylketonuria, an inherited disorder that can cause mental retardation or even death. A 0.085 M solution of C6H5CH2COOH has a pH of 2.68. Calculate the Ka value for this acid.
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 55
A particular sample of vinegar has a pH of 2.90. If acetic acid is the only acid that vinegar contains (Ka = 1.8 * 10^-5), calculate the concentration of acetic acid in the vinegar.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand that pH is a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration \([H^+]\) in a solution. Use the formula \(pH = -\log[H^+]\) to find \([H^+]\).
Step 2: Rearrange the formula to solve for \([H^+]\): \([H^+] = 10^{-pH}\). Substitute the given pH value of 2.90 into this equation to calculate \([H^+]\).
Step 3: Recognize that acetic acid \((CH_3COOH)\) is a weak acid and partially dissociates in water according to the equation: \(CH_3COOH \rightleftharpoons CH_3COO^- + H^+\).
Step 4: Use the expression for the acid dissociation constant \(K_a\) for acetic acid: \(K_a = \frac{[CH_3COO^-][H^+]}{[CH_3COOH]}\). Assume \([CH_3COO^-] = [H^+]\) at equilibrium since each mole of acetic acid that dissociates produces one mole of \(H^+\) and one mole of \(CH_3COO^-\).
Step 5: Substitute \([H^+]\) from Step 2 and \(K_a = 1.8 \times 10^{-5}\) into the \(K_a\) expression to solve for the initial concentration of acetic acid \([CH_3COOH]\).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pH and pKa
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration. The pKa is the negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (Ka) and indicates the strength of an acid; lower pKa values correspond to stronger acids. Understanding the relationship between pH and pKa is essential for calculating the concentration of acids in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The pH Scale
Acid Dissociation Constant (Ka)
The acid dissociation constant (Ka) quantifies the strength of an acid in solution, representing the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the acid into its ions. For acetic acid, the dissociation can be expressed as CH3COOH ⇌ H+ + CH3COO-. A higher Ka value indicates a stronger acid, while a lower value suggests a weaker acid. This concept is crucial for determining the concentration of acetic acid from the given pH.
Recommended video:
Guided course
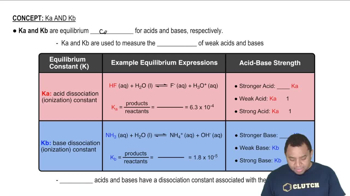
Characteristics of Ka and Kb
Concentration Calculations
Concentration calculations involve determining the amount of solute present in a given volume of solution. In this context, the concentration of acetic acid can be derived from the pH and the Ka value using the formula that relates pH to the concentration of hydrogen ions and the dissociation of the acid. This process often requires rearranging equations and applying the principles of equilibrium to find the unknown concentration.
Recommended video:
Guided course
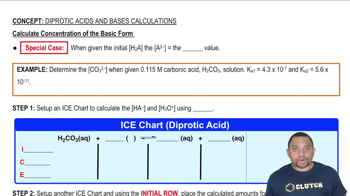
Calculate Concentration of the Basic Form
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A 0.100 M solution of chloroacetic acid 1ClCH2COOH2 is 11.0% ionized. Using this information, calculate 3ClCH2COO-4, 3H+4, 3ClCH2COOH4, and Ka for chloroacetic acid.
Textbook Question
A 0.100 M solution of bromoacetic acid 1BrCH2COOH2 is 13.2% ionized. Calculate 3H+4, 3BrCH2COO-4, 3BrCH2COOH4 and Ka for bromoacetic acid.
Textbook Question
If a solution of HF 1Ka = 6.8 * 10-42 has a pH of 3.65, calculate the concentration of hydrofluoric acid.
Textbook Question
The acid-dissociation constant for chlorous acid 1HClO22 is 1.1 * 10-2. Calculate the concentrations of H3O+, ClO2-, and HClO2 at equilibrium if the initial concentration of HClO2 is 0.0125 M.
