Textbook Question
In Section 11.5, we defined the vapor pressure of a liquid in terms of an equilibrium. (a) Write the equation representing the equilibrium between liquid water and water vapor and the corresponding expression for Kp.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
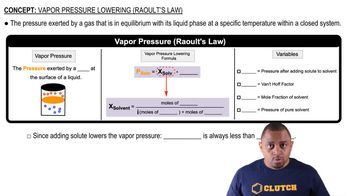


In Section 11.5, we defined the vapor pressure of a liquid in terms of an equilibrium. (a) Write the equation representing the equilibrium between liquid water and water vapor and the corresponding expression for Kp.
In Section 11.5, we defined the vapor pressure of a liquid in terms of an equilibrium. (b) By using data in Appendix B, give the value of Kp for this reaction at 30 C.