Textbook Question
Ozone, O3, decomposes to molecular oxygen in the stratosphere according to the reaction 2 O31g2¡3 O21g2. Would an increase in pressure favor the formation of ozone or of oxygen?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Ozone, O3, decomposes to molecular oxygen in the stratosphere according to the reaction 2 O31g2¡3 O21g2. Would an increase in pressure favor the formation of ozone or of oxygen?
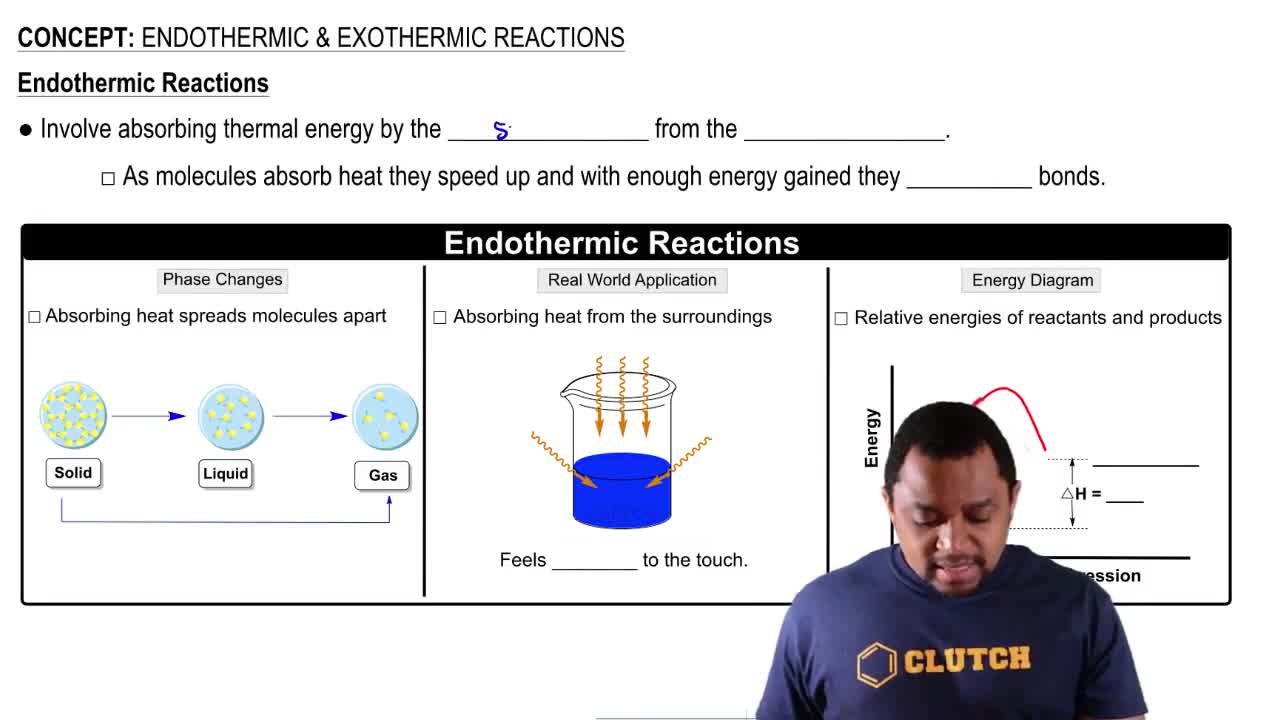
(a) Is the dissociation of fluorine molecules into atomic fluorine, F2(𝑔) ⇌ 2 F(𝑔), an exothermic or endothermic process?