Textbook Question
What is the molecularity of each of the following elementary reactions? Write the rate law for each. (a) Cl2(g) → 2 Cl(g)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

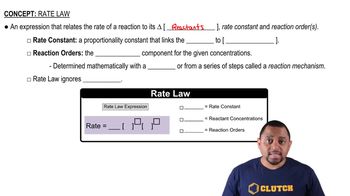
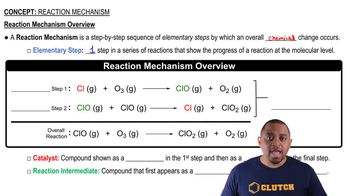
What is the molecularity of each of the following elementary reactions? Write the rate law for each. (a) Cl2(g) → 2 Cl(g)
(b) What is the difference between a unimolecular and a bimolecular elementary reaction?
What is the molecularity of each of the following elementary reactions? Write the rate law for each. (c) NO(g) + Cl2(g) → NOCl2(g)
What is the molecularity of each of the following elementary reactions? Write the rate law for each.
(a) 2 NO(g) → N2O2(g)
(c) SO3(g) → SO2(g) + O(g)
What is the molecularity of each of the following elementary reactions? Write the rate law for each. (b)