The reaction between ethyl iodide and hydroxide ion in ethanol (C2H5OH) solution, C2H5I(alc) + OH-(alc) → C2H5OH(l) + I-(alc), has an activation energy of 86.8 kJ/mol and a frequency factor of 2.10 × 1011 M-1 s-1. (c) Which reagent in the reaction is limiting, assuming the reaction proceeds to completion?

The reaction between ethyl iodide and hydroxide ion in ethanol solution, C2H5I(alc) + OH-(alc) → C2H5OH(l) + I-(alc), has an activation energy of 86.8 kJ/mol and a frequency factor of 2.10 × 10^11 M^-1 s^-1. (b) A solution of KOH in ethanol is made up by dissolving 0.335 g KOH in ethanol to form 250.0 mL of solution. Similarly, 1.453 g of C2H5I is dissolved in ethanol to form 250.0 mL of solution. Equal volumes of the two solutions are mixed. Assuming the reaction is first order in each reactant, what is the initial rate at 35 _x001E_C?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Activation Energy
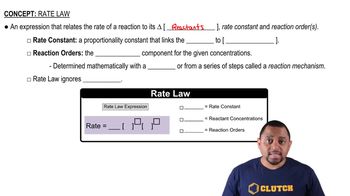
Rate Law and Reaction Order
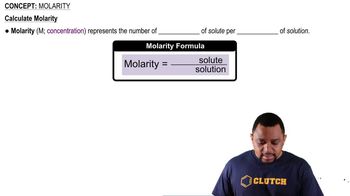
Concentration and Molarity
Enzymes are often described as following the two-step mechanism:
E + S ⇌ ES (fast)
ES → E + P (slow)
where E = enzyme, S = substrate, ES = enzyme9substrate complex, and P = product.
(a) If an enzyme follows this mechanism, what rate law is expected for the reaction?
Enzymes are often described as following the two-step mechanism:
E + S ⇌ ES (fast)
ES → E + P (slow)
where E = enzyme, S = substrate, ES = enzyme9substrate complex, and P = product.
(b) Molecules that can bind to the active site of an enzyme but are not converted into product are called enzyme inhibitors. Write an additional elementary step to add into the preceding mechanism to account for the reaction of E with I, an inhibitor.
The reaction between ethyl iodide and hydroxide ion in ethanol (C2H5OH) solution, C2H5I(alc) + OH-(alc) → C2H5OH(l) + I-(alc), has an activation energy of 86.8 kJ/mol and a frequency factor of 2.10 × 1011 M-1 s-1. (d) Assuming the frequency factor and activation energy do not change as a function of temperature, calculate the rate constant for the reaction at 50 C.
The gas-phase reaction of NO with F2 to form NOF and F has an activation energy of Ea = 6.3 kJ/mol. and a frequency factor of A = 6.0 × 108 M-1 s-1. The reaction is believed to be bimolecular: NO(g) + F2(g) → NOF(g) + F(g) (b) Draw the Lewis structures for the NO and the NOF molecules, given that the chemical formula for NOF is misleading because the nitrogen atom is actually the central atom in the molecule.
